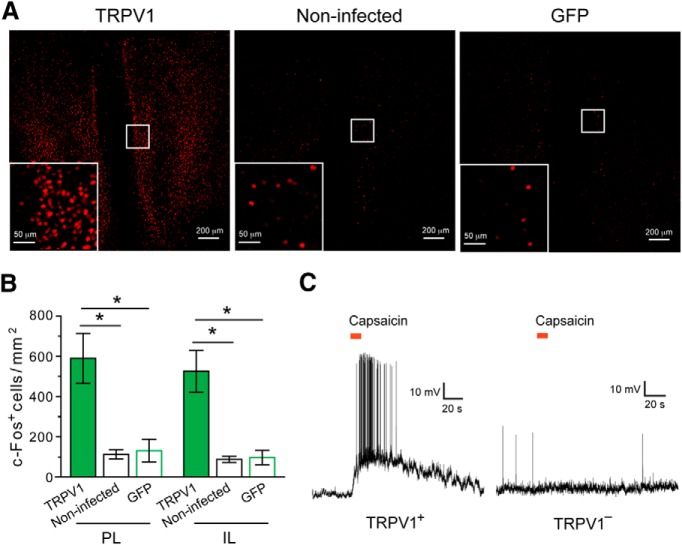
Figure 6.
TRPV1-mediated activation of mPFC neurons in the ROSA-stopflox-TRPV1;TRPV1−/− mice. A, Representative images of c-Fos expression in the mPFC after capsaicin treatment. Left, ROSA-stopflox-TRPV1;TRPV1−/− mice in which the mPFC was injected with AAV-GFP-IRES-Cre (to activate TRPV1 expression). Middle, ROSA-stopflox-TRPV1;TRPV1−/− mice that did not receive viral injection. Right, ROSA-stopflox-TRPV1;TRPV1−/− mice in which the mPFC was injected with AAV-GFP. Inset, Higher-magnification image of the boxed area. c-Fos was recognized by an antibody. B, Capsaicin treatment activated mPFC neurons as indicated by c-Fos expression in both PL and IL areas. C, The mPFC of ROSA-stopflox-TRPV1;TRPV1−/− mice was injected with AAV-GFP-IRES-Cre to induce TRPV1 expression. Puffs of capsaicin (8 μm, indicated by the red bars) applied to the cell body induced a robust increase in spiking activity in the majority of TRPV1-positive (TRPV1+) mPFC neurons (10 of 12 neurons from 6 mice) (left) but did not change activity in any of the TRPV1-negative (TRPV1−) mPFC neurons recorded (13 of 13 neurons from 6 mice) (right). *p < 0.05.