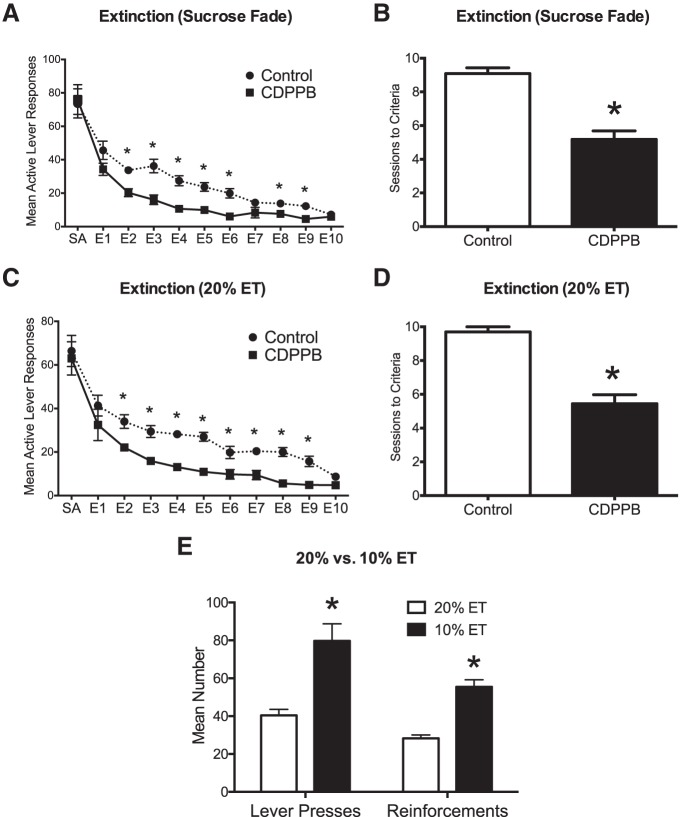
Figure 1.
Treatment with CDPPB during extinction training facilitates the acquisition of extinction learning. Rats were trained to self-administer ethanol using a sucrose-fading technique (average ethanol consumption in 30 min was 1.18 g/kg; A and B; n = 11). A separate group of rats were trained to self-administer ethanol using a 2-bottle intermittent access initiation procedure (average consumption in 30 min was 1.11 g/kg; C and D; n = 10). CDPPB resulted in a significant reduction in active lever responding on multiple days during extinction training and significantly decreased the number of sessions required to reach extinction criteria. *p = 0.001. E, In rats trained to self-administer ethanol, reducing the concentration of ethanol in the operant session from 20% to 10% resulted in a significant increase in both active lever responses (*p = 0.001) and number of reinforcements received (*p = 0.002; n = 10).