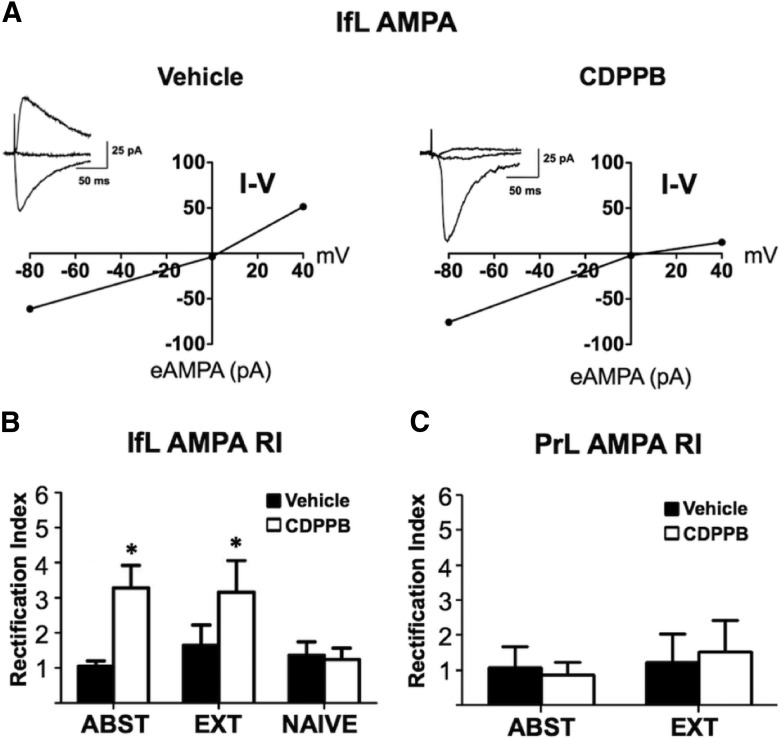
Figure 7.
CDPPB induces the formation of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors in the IfL only in rats with a history of ethanol self-administration. Rats were trained to self-administer ethanol using an ethanol pre-exposure paradigm and then administered vehicle or CDPPB during abstinence (ABST) or extinction training (EXT). A, When the holding potential was stepped from −80 to +40 mV, the I–V plots for eAMPA currents revealed that CDPPB treatment with and without extinction training shifted the AMPA currents from nonrectifying (calcium-impermeable) to rectifying (calcium-permeable) only in the IfL cortex. The insets represent traces of evoked AMPA currents at holding potentials of −80, 0, and +40 mV. B, C, Comparison of the AMPA current RI revealed that, in the IfL cortex, CDPPB treatment increased rectification (p = 0.001) in both the ABST and EXT groups, but had no effect when administered to ethanol-naive rats. Neither CDBBP nor extinction training altered AMPA current rectification in the PrL cortex. Asterisk indicates significant difference from the respective vehicle control for ABST (p = 0.004) and EXT (p = 0.048) groups (n = 6 for all groups except CDPPB/Naive, n = 8).