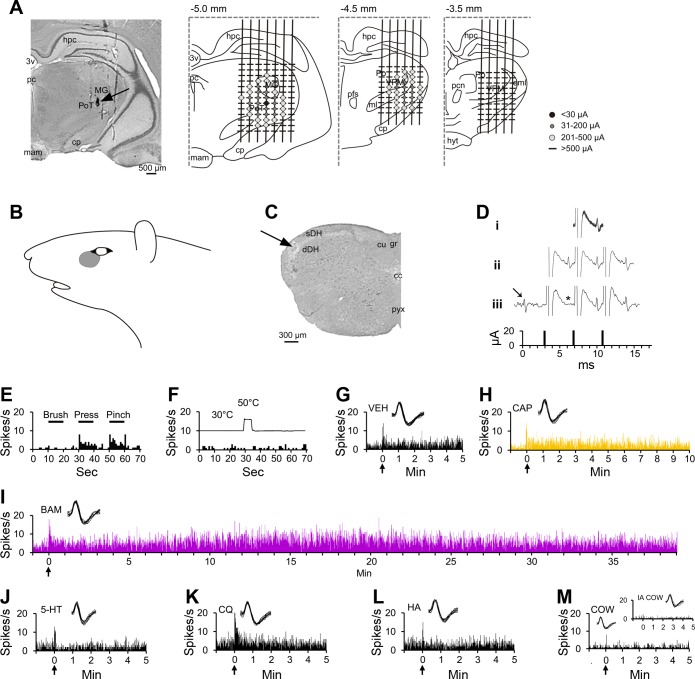
Fig. 1.
Characterization of a pruriceptive trigeminothalamic tract (VTT) neuron responding to BAM8–22 and capsaicin. A: lesion (arrow) made at the point in the thalamus with the lowest threshold for antidromic activation. Drawings indicate the location of each antidromic test site at 3 rostral-caudal planes within the thalamus; threshold for antidromic activation at each point is indicated by the color/size of the marker at each point (see legend). Numbers above each drawing indicate distance caudal to bregma. B: receptive field. C: lesion (arrow) made at the recording point in the superficial layers of the spinal trigeminal nucleus. D: antidromic spikes have a fixed latency from the antidromic stimulus (i), follow a high-frequency stimulus train (ii), and an orthodromic spike (arrow) collides with an antidromic spike (expected location indicated by *; iii). E: responses to mechanical stimulation of the receptive field (black bar above histogram indicates duration of mechanical stimulus). F: response to thermal stimulation of the receptive field (trace above histogram indicates onset and duration of 50°C thermal stimulus). G: intradermal injection (indicated by arrow) of vehicle into the receptive field produced no sustained response. H–I: the cell responded to the partial pruritogen capsaicin and to the pruritogen BAM8–22, each injected intradermally into the receptive field. Responses are colored differently according to chemical, so that data regarding a single pruritogen or partial pruritogen can be more easily identified throughout the following figures. J–M: the cell did not respond to intradermal injection of serotonin, chloroquine, or histamine, or to application of cowhage spicules (M, inset: response to heat-inactivated cowhage). For this cell, pruritogens and partial pruritogens were applied in the following order: cowhage (COW), BAM8–22 (BAM), chloroquine (CQ), histamine (HA), serotonin (5-HT), and capsaicin (CAP). Insets: 10 randomly selected overlaid spike traces. 3v, third ventricle; cc, central canal; cp, cerebral peduncle; cu, cuneate fasciculus; dDH, deep dorsal horn; eml, external medullary lamina; gr, gracile fasciculus; hpc, hippocampus; hyt, hypothalamus; mam, mammillary n.; MG, medial geniculate n.; ml, medial lemniscus; pc, posterior commissure; pcn, paracentral n.; pfs, parafascicular n.; Po, posterior thalamic n.; PoT, posterior triangular n.; pyx, pyramidal decussation; sDH, superficial dorsal horn; VPM, ventroposterior medial n.