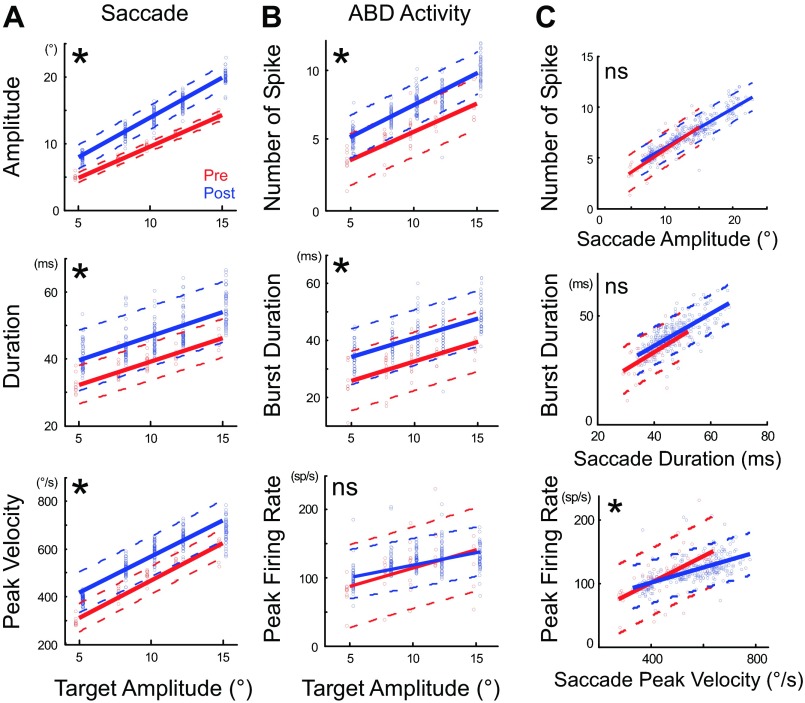
Fig. 3.
Effect of cFN inactivation on the attributes of ipsiversive saccades and the activity of an agonist ABD neuron (unit 14). A: graphs of the saccade amplitude (top), duration (middle), and peak velocity (bottom) as a function of target amplitude. B: graphs of the number of spikes (top), burst duration (middle), and peak firing rate (bottom) in the example ABD neuron as a function of target amplitude. Regression lines of pre- (red) and postinactivation (blue) are significantly different in all except peak firing rate (*P < 0.05; ns, not significant). Each point indicates 1 saccade. We shifted the blue postinactivation points slightly rightward and red preinactivation points slightly leftward to make them distinguishable. C: relationship between the agonist ABD activity and ipsiversive saccade attributes before (red) and after (blue) cFN inactivation. Top shows relationship between the number of spikes and saccade amplitude, middle between burst duration and saccade duration, and bottom between peak firing rate and saccade peak velocity. Regression lines of pre- and postinactivation are not significantly different in both number of spikes vs. amplitude and burst duration vs. saccade duration but differ significantly in peak firing rate vs. peak velocity (P < 0.05).