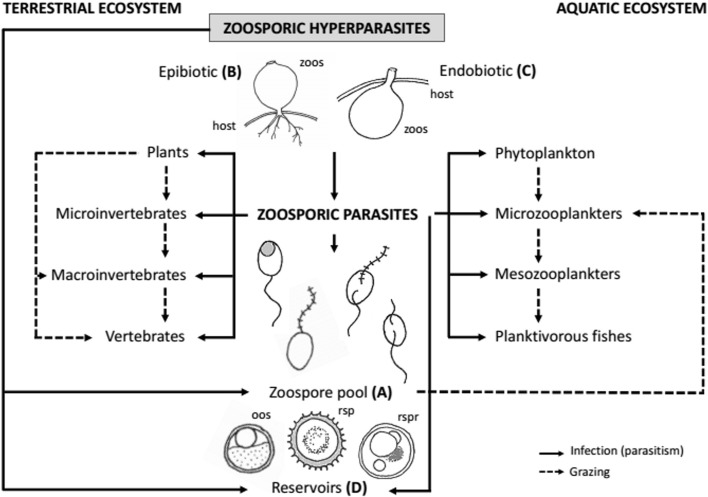
Figure 2.
Possible links of a hypothesized food web in which zoosporic parasites and hyperparasites are involved. In food webs zoosporic hyperparasites can either contribute the zoospore pool (Zoospore pool, A) which is used as food source by grazers in terrestrial and acquatic ecosystems. At the same time epibiotic sporangia of hyperparasites (Epibiotic, B) can serve as food source for larger grazers. The sporangia of epibiotic hyperparasites (Endobiotic, C) are more difficult to access as food sources for grazers. Some zoosporic hyperparasites use resting stages (Reservoirs, D) as substrate. Hosts of hyperparasites can be parasites of microscopic eukaryotes, but also parasites of plants or animals. This allows for a rapid cycling of nutrients from organisms higher up in the food web towards small grazers (trophic upgrading). References: zoos, zoosporangium; host, zoosporic host; oos, oospore; rsp, resting spore; rspr, resting sporangium.