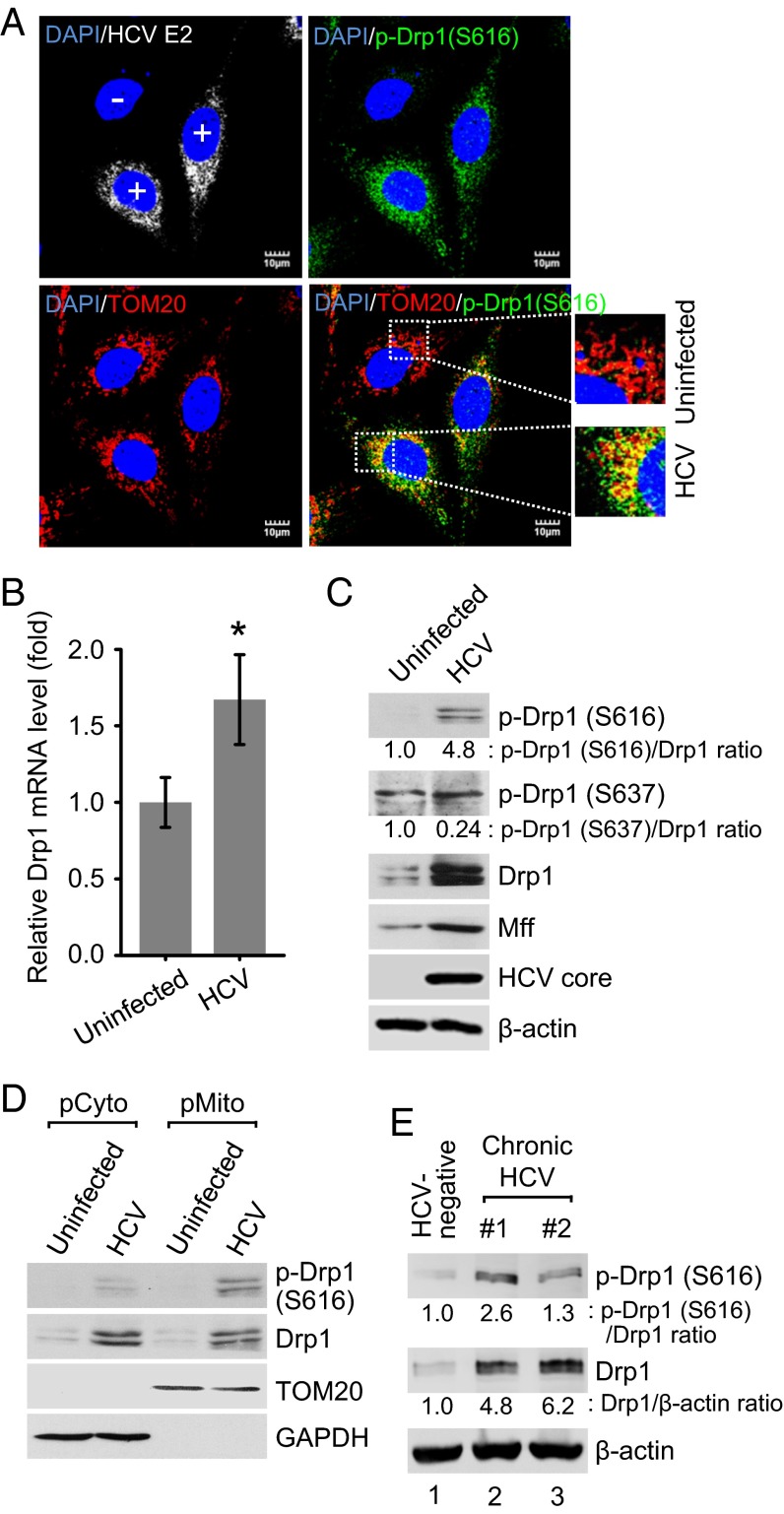
Fig. 2.
HCV stimulates the expression of Drp1 and Mff and promotes Drp1 Ser616 phosphorylation and subsequent translocation to mitochondria. (A) Immunofluorescence analysis showing the induction of Drp1 Ser616 phosphorylation and its localization on the mitochondria in HCV-infected cells. At 2 d postinfection, HCV-infected Huh7 cells were immunostained with antibodies specific to TOM20 (red), p-Drp1 (Ser616) (green), and HCV E2 protein (white). In the zoomed images, yellow spots indicate the merge of p-Drp1 (Ser616) with mitochondria. Infected cells, +; uninfected cells, −. Nuclei, DAPI (blue). (B–D) Analyses of Drp1 mRNA level (B) and protein expression (C and D). Huh7 cells infected with HCVcc (MOI, 5) were used for RNA analysis by qRT-PCR at 1 d postinfection (mean ± SD; n = 3; *P ≤ 0.01, by unpaired Student t test) (B) and protein expression at 5 d postinfection (C). (D) Western blot analysis of purified subcellular fractions from uninfected (mock) and HCV-infected cells. Fractions: purified cytosolic, pCyto; purified mitochondria, pMito. Organelle markers: TOM20, mitochondria; GAPDH, cytoplasm. (E) Western blot analysis of p-Drp1 (S616) and total Drp1 expression levels in liver biopsies of chronic hepatitis C patients. Lane 1, HCV-negative; lanes 2–3, HCV-positive. β-actin, protein-loading control. (C and E) The band intensities were analyzed by ImageJ software.