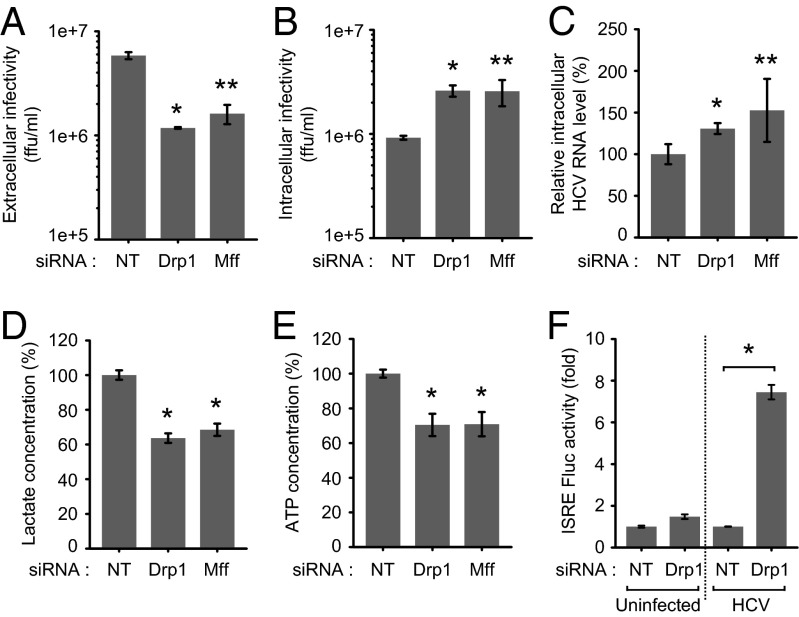
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of mitochondrial fission affects HCV secretion and innate immune response. (A–E) Huh7 cells transfected with nontargeting (NT) or gene-specific siRNA pools targeting Drp1 and Mff, respectively, were infected HCVcc (MOI, 5). At 3 d postinfection, culture medium and cells were used for analyses of extracellular infectivity (A) and intracellular infectivity (B) determined by Foci-forming unit assay, intracellular HCV RNA levels (C) analyzed by qRT-PCR, lactate concentration (D) determined by cell-based glycolysis assay kit, and intracellular ATP levels (E) determined by the ATP EnzyLight assay kit (mean ± SEM; n = 3; *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.005, by unpaired Student t test). (F) Drp1 silencing increases ISRE promoter activity in HCV-infected cells. Huh7 cells cotransfected with plasmids encoding ISRE Firefly luciferase reporter and wild-type Renilla luciferase reporter were subsequently transfected with NT or Drp1-specific siRNA pools and, 12 h later, infected with HCVcc (MOI, 5). At 2 d postinfection, the relative ISRE-luciferase activity was determined as described in Materials and Methods (mean ± SD; n = 3; *P ≤ 0.01, by unpaired Student t test).