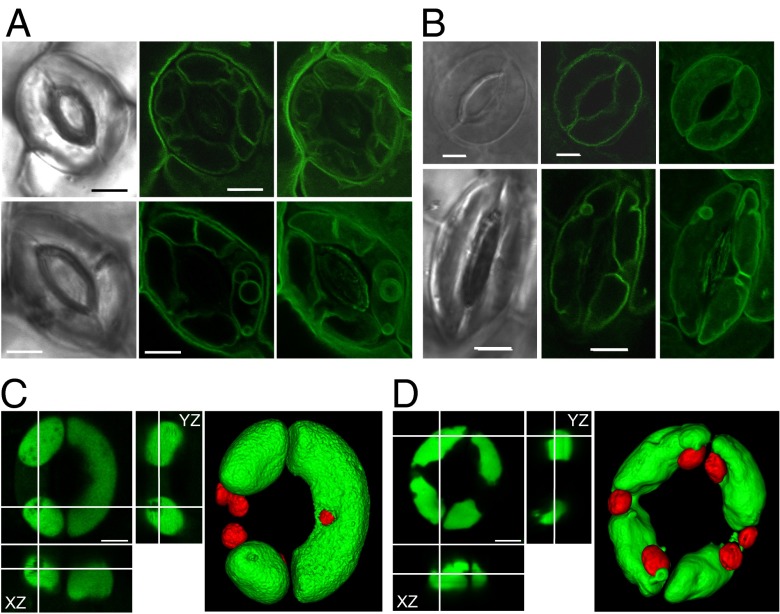
Fig. 7.
Alleviation of vacuolar dysfunction by sodium. (A) Vacuolar structure of nhx1 nhx2 guard cells visualized with TIP1;1:GFP during stomatal opening. Pictures were taken after illumination for 2 h in the presence of 10 mM KCl (Upper) or 50 mM of NaCl (Lower). Bright-field (Left) and GFP images (Center) and 3D projection of z-axis images (Right) of TIP1;1:GFP. (Scale bar: 5 µm.) (B) Vacuolar structure in guard cells of the transgenic line expressing NHX2:GFP after illumination for 2 h (Upper) and after 2 h of incubation in darkness (Lower). The incubation buffer contained 10 mM KCl. Bright-field (Left) and GFP images (Center) and a 3D projection of z-axis images (Right) of NHX2:GFP. (Scale bar: 5 µm.) (C) Orthogonal views and 3D surface rendering of z-axis images of WT guard cell vacuoles loaded with 10 μM of BCECF-AM. Pictures were taken after illumination for 3 h in the presence of 50 mM of NaCl. (Scale bar: 5 µm.) (D) Orthogonal views and 3D surface rendering of z-axis images of the nhx1 nhx2 guard cell vacuoles loaded with 10 μM of BCECF-AM. Pictures were taken after illumination for 3 h in the presence of 50 mM of NaCl. (Scale bar: 5 µm.)