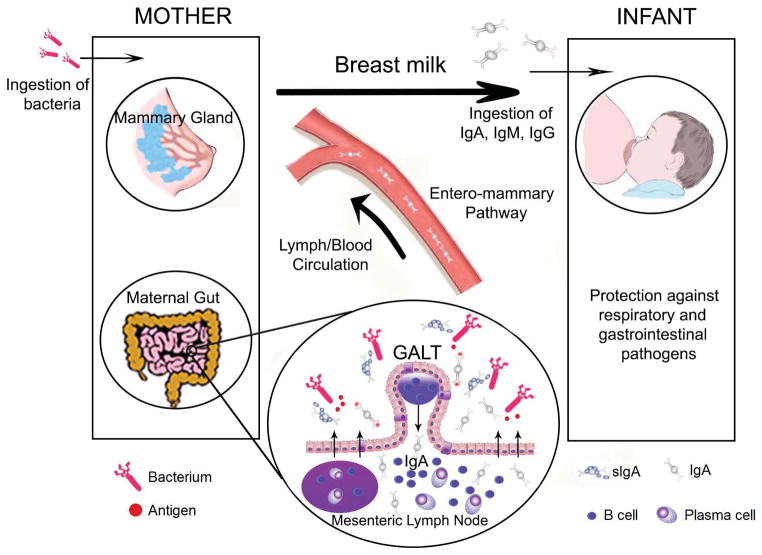
Fig. 1. Integration of mucosal immunity between mother and the newborn.
Migration of effector B cells from the gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) via lymph and peripheral blood to the lactating mammary gland. The distribution of B cells beyond the gut (arrows) is crucial for local production in breast milk of sIgA antibodies specific for enteric and airway microorganisms (Modified from Brandtzaeg P, 2010) [31]. There is also transmission of organisms/bioactive compounds from the child to the mother which induces responses from the mother that are specific to the child’s needs (two way path) [54].