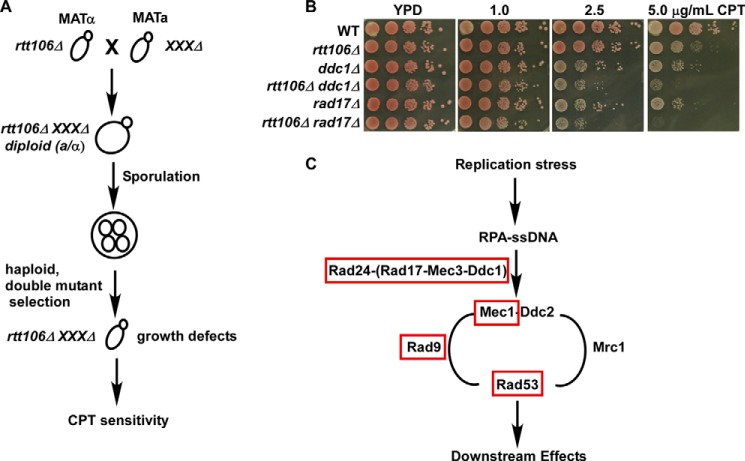
FIGURE 1.
RTT106 genetically interacts with each component of the RAD17-MEC3-DDC1 complex in response to the topoisomerase I inhibitor, CPT. A, identification of RTT106 genetic interactors in response to CPT treatment using the synthetic genetic array method. Double mutants containing rtt106Δ and each of ∼4700 nonessential deletion mutants were generated, and viable double mutants were assessed for growth defects in medium with or without low concentrations of CPT. Candidate genes were selected in which double mutants exhibited no apparent growth defects in normal growth medium but a severe growth defect in CPT-containing medium. B, RTT106 and the 9-1-1 complex exhibited a synthetic interaction in response to CPT. Fresh cells of the indicated genotype (WT = wild type) were spotted onto regular growth medium or medium containing low concentrations of CPT. Growth was assessed over several days with the representative images shown. C, the rtt106Δ mutant exhibited genetic interactions with mutations at genes involved in the S phase DNA damage checkpoint but not the DNA replication checkpoint. A schematic summary of the genetic analyses performed for rtt106Δ in combination with mutants of each of the factors indicated in response to CPT. Genes marked in red genetically interacted with RTT106, whereas genes marked in black did not. Genetic interactions were determined using a DNA damage sensitivity spot assay and are described in Table 1.