FIGURE 6.
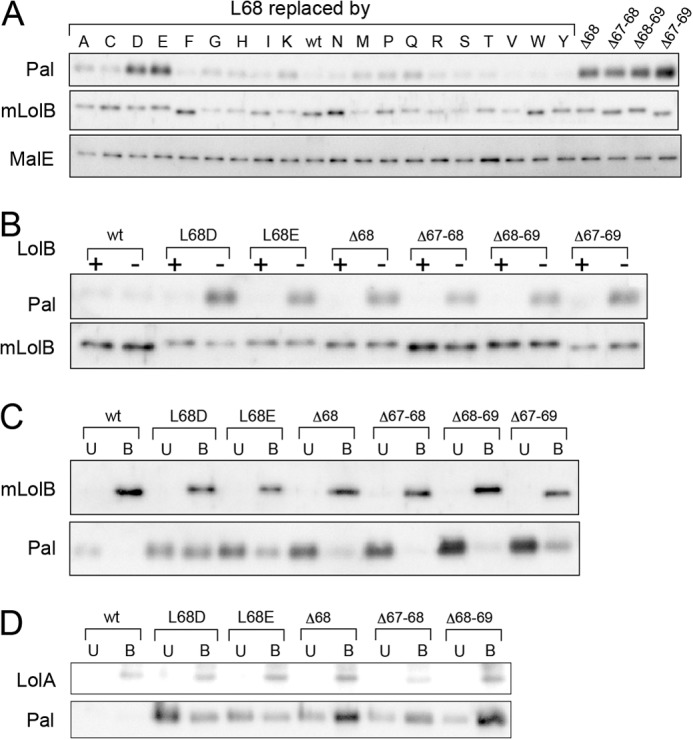
Defective mLolB(His) derivatives cause accumulation of Pal in the periplasm as a complex with mLolB or LolA. A, KT50 cells harboring pRT102 derivatives were grown on LB broth supplemented with 50 μm IPTG at 30 °C. The levels of Pal, mLolB(His), and MalE in the periplasmic fraction prepared from the cells were determined by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies against the respective proteins. B, KT50 cells harboring pRT102 derivatives encoding L68D/L68E and the four deletion mutants were transformed with (+) or without (−) pNAS021 encoding LolB. The levels of Pal and mLolB(His) in the periplasm were then examined as in A. wt, wild type. C, a periplasmic fraction of KT50 cells harboring pRT102 was prepared as in A and applied to TALON resin to adsorb mLolB(His) derivatives. The resin bound (B) and unbound (U) fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-LolB and -Pal antibodies as described under “Experimental Procedures.” D, the periplasmic fraction mentioned in C was treated with anti-LolA antibodies followed by binding to protein A resin. The resin bound (B) and unbound (U) fractions were analyzed as in C except with anti-LolA and -Pal antibodies.
