FIGURE 1.
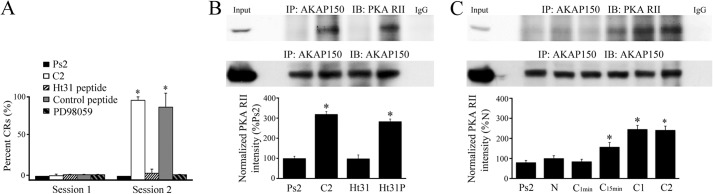
An interaction between PKA and the scaffolding protein AKAP is required for conditioning. A, percent acquisition of CRs in the first and second pairing sessions for preparations that underwent pseudoconditioning for two sessions (Ps2), conditioning for two pairing sessions (C2), treatment with the PKA inhibitory peptide Ht31 (10 μm), a control peptide (Ht31P, 10 μm), or the MEK-ERK inhibitor PD98059 (50 μm) for two sessions of conditioning is shown. Treatment with Ht31 or PD98059 resulted in no conditioning. *, significant differences from Ps2 (p < 0.0001). B, immunoprecipitation of AKAP150 with the PKA RII binding domain was greatly enhanced after conditioning at C2. Treatment with the Ht31 peptide during two conditioning sessions disrupted the PKA-AKAP interaction but the control peptide showed little effect compared with normal conditioning. *, significant differences from Ps2. C, timing of the onset of the PKA-AKAP protein interaction during conditioning. Significant binding was detected after 15 min of conditioning but not earlier and was maintained throughout the training procedure. Input (whole cell lysates from naïve) and IgG lanes are also shown in B and C. N, naïve untrained preparations, C1min, 1 min of conditioning (2 stimuli), C15min, 15 min of conditioning, C1, one session of conditioning (25 min), C2, two sessions of conditioning (80 min). *, significant differences compared with N, which was 100%. In this and all figures, the n and p values are given in the text.
