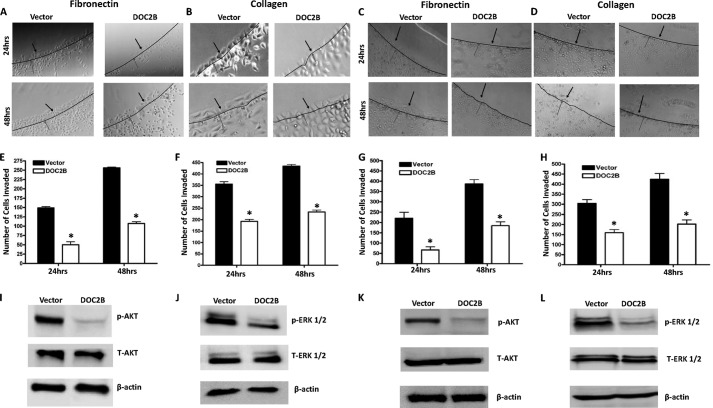
FIGURE 7.
DOC2B inhibits invasion and phosphorylation of AKT-1 and ERK1/2. A–D, representative images showing the inhibition of invasion onto the agarose spot containing fibronectin and type I collagen upon ectopic expression of DOC2B in a single cell clone (A and B) and retrovirally transduced polyclonal cells (C and D). E–H, quantitative analysis of a number of tumor cells invading fibronectin and type 1 collagen in a single cell clone (E and F) and retrovirally transduced polyclonal cells (G and H), respectively. The bar graph represents mean ± S.D. of triplicate experiments performed in duplicates. *, p < 0.05 by independent Student's t test was considered as statistically significant. I–L, ectopic expression of DOC2B regulated both AKT and ERK signaling. A Western blot was performed using antibodies against total AKT, phospho-AKT, total ERK1/2, and phospho-ERK1/2. β-Actin was used as internal control. DOC2B expression inhibited AKT phosphorylation, whereas there was a decrease in ERK1/2 phosphorylation when compared with vector-transfected control SiHa cells in both single cell clone (I and J) and polyclonal cells (K and L), respectively. Relative phosphorylation levels of AKT and ERK1/2 were determined by normalization with total AKT and total ERK1/2, respectively.