FIGURE 6.
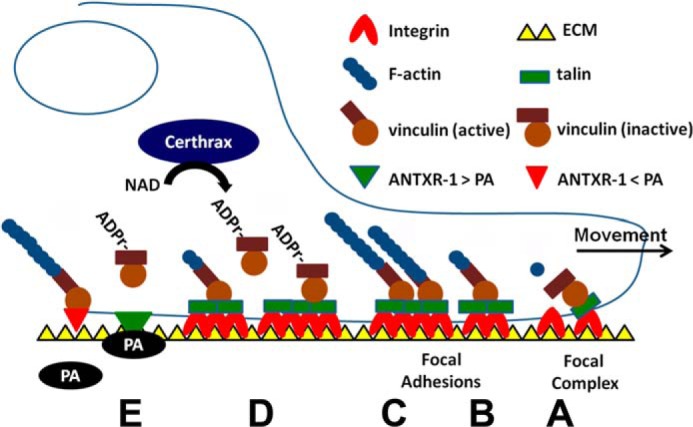
How Certhrax may stimulate actin depolymerization, cell detachment, and potential synergy with anthrax toxin. A, in a normal cell, talin recruits inactive vinculin to focal complexes. B, vinculin associates with PIP2, actin, or other binding partners, which leads to complete activation of vinculin; otherwise, vinculin is released back into the cytosol. C, vinculin binding to talin stabilizes an active conformation of integrins in focal adhesions, which allow vinculin to form a coherent contact between the ECM and promote polymerization of actin stress fibers. D, upon Certhrax intoxication, vinculin is ADP-ribosylated, and ADP-r-vinculin is lost from the focal adhesion site, which stimulates focal adhesion complex disruption. E, actin depolymerization may enhance PA affinity for the anthrax toxin receptor, increasing G9241 virulence. (Modified with permission from Humphries et al. (24).) Vinculin controls focal adhesion formation by direct interactions with talin and actin.
