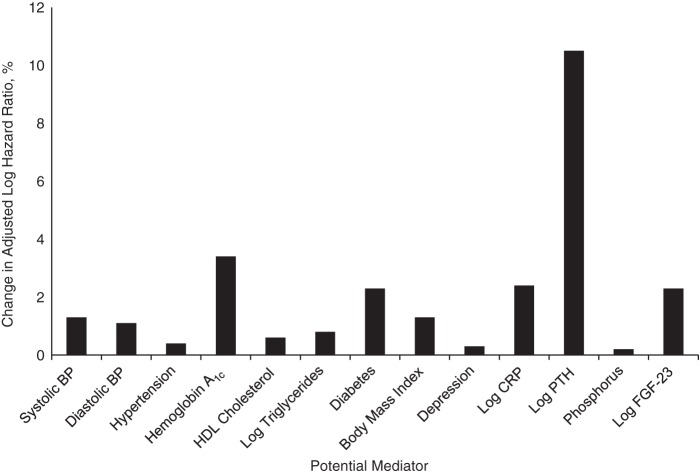
Figure 3.
Change in the strength of the association between 25-hydroxyvitamin D level (<20 ng/mL vs. ≥20 ng/mL) and cardiovascular events after adjustment for potential mediators (expressed as percent change in the age-adjusted log hazard ratio) among 946 participants in the Heart and Soul Study, 2000–2012. All models adjusted for sociodemographic factors (age, sex, white race/ethnicity, season of blood draw, and college graduation) and health behaviors (tobacco use, multivitamin use, and physical activity). BP, blood pressure; CRP, C-reactive protein; FGF-23, fibroblast growth factor 23; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; PTH, parathyroid hormone.