Figure 2.
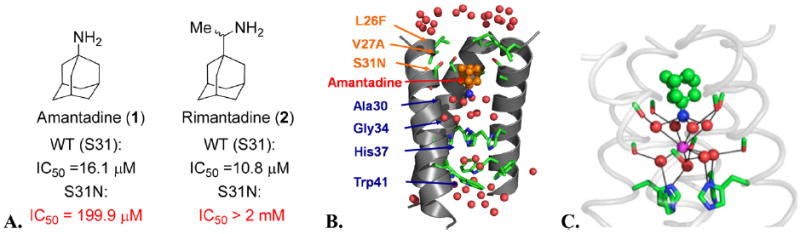
(A) Activity of amantadine and rimantadine against the WT (S31) and S31N mutant in the TEVC assay. (B) The M2 channel-lining residues found in transmissible drug-resistant mutants are shown in orange letters. Amantadine (orange bound drug) causes a break in the aqueous path (water molecules, red balls). One helix has been removed for clarity. (C) Snapshot from a simulation of amantadine with WT.15 Water molecules (red) associate with carbonyl groups (green/red sticks) in a square planar array. This array of water molecules can stabilize the bound ammonium group of amantadine (green and blue bound drug) or a centrally located water molecule (magenta).
