FIGURE 3.
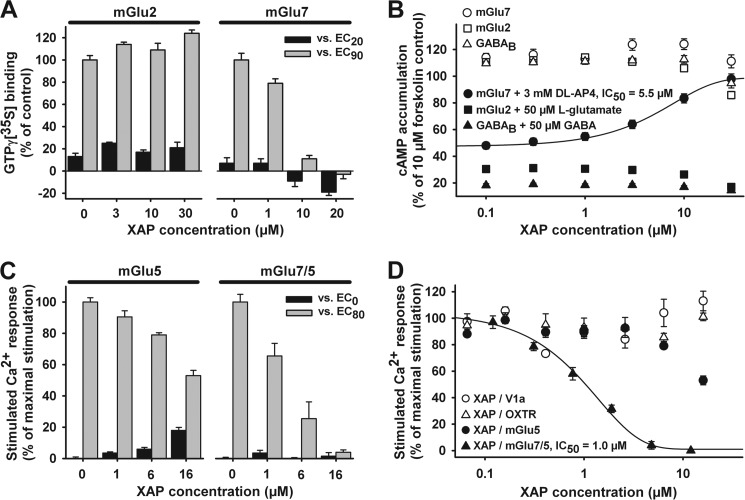
Potency, mGlu7 selectivity, efficacy, and assay independence of XAP044. A, effect of increasing concentrations of XAP044 (XAP) on [35S]GTPγS (GTPγ[35S]) binding in the presence of submaximal concentrations of l-glutamate (EC20 = 1 μm and EC90 = 50 μm) using membranes from CHO cells stably expressing mGlu2 or of DL-AP4 with mGlu7 membranes (EC20 = 100 μm and EC90 = 4000 μm). B, concentration-dependent effect of XAP044 on the inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation in CHO cells stably expressing mGlu7, mGlu2, or GABAB in the absence (open symbols) or presence (filled symbols) of 3 mm DL-AP4, 50 μm l-glutamate, or 50 μm GABA, respectively; all data are normalized to the control stimulation of 10 μm forskolin (set to 100%). C, effect of increasing concentrations of XAP044 on the Ca2+ response of mammalian cells in the absence and presence of near-maximal concentrations of l-glutamate (EC80 = 10 μm) or DL-AP4 (EC80 = 4000 μm) using L cells stably expressing mGlu5a or CHO cells expressing the chimeric receptor mGlu7/5a, respectively. D, concentration-response curves for inhibition of agonist (EC80–90)-stimulated Ca2+ responses by XAP044 in stable cell lines expressing the V1a receptor, the oxytocin receptor, mGlu5a, or the chimeric receptor mGlu7/5a. All data represent the mean ± S.E. from at least three independent measurements (n ≥ 3) normalized to the control stimulation of EC80–90 of the respective control agonists (set to 100%; A, C, and D) or 10 μm forskolin control (B).