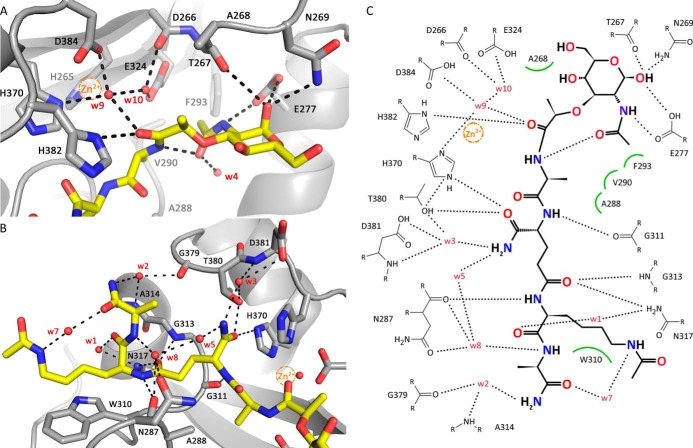
FIGURE 3.
Interactions between AmiA-cat and MtetP. A, interactions of AmiA-cat with the MurNAc moiety and l-Ala of MtetP at the active site. The zinc ion from the native structure (orange sphere) is superimposed on the AmiA-cat complex (gray) with MtetP (yellow). B, close-up of the interactions of the peptide moiety of MtetP with AmiA. C, ChemSketch (57) plot of interactions between MtetP and AmiA-cat. Van-der-Waals interactions are depicted as green arcs, and hydrogen bonds are shown as black dashed lines. Coordination of Wat-9 involves His-370, Asp-384, and Wat-10 and a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl oxygen of the scissile amide bond in the ligand, which itself is positioned by interaction with His-382. Wat-10 lies next to Asp-266, Glu-324, Wat-9, and the carbonyl carbon of the scissile bond. MurNAc forms an intramolecular and four further hydrogen bonds with Glu-277, Thr-267, and Asn-269. Hydrophobic interactions of the methyl groups involve Ala-268 and Phe-293, respectively. l-Ala inserts into a small hydrophobic pocket formed by residues Ala-288 and Val-290. The amide side chain of d-iGln forms direct hydrogen bonds with Thr-380 and His-370 as well as two water-mediated hydrogen bonds to Asp-381. The carbonyl oxygen bonds with Gly-313 and Asn-317. l-Lys is stabilized by interactions with Asn-287 as well as Asn-317, whereas the acetylated side chain engages in hydrophobic interactions with Trp-310. A water (Wat-7 (w7)) bridges Nϵ of l-Lys-NHAc and the carbonyl oxygen of d-Ala, which engages additional water-mediated interactions with AmiA-cat residues Asn-287, Ala-314, and Gly-379.