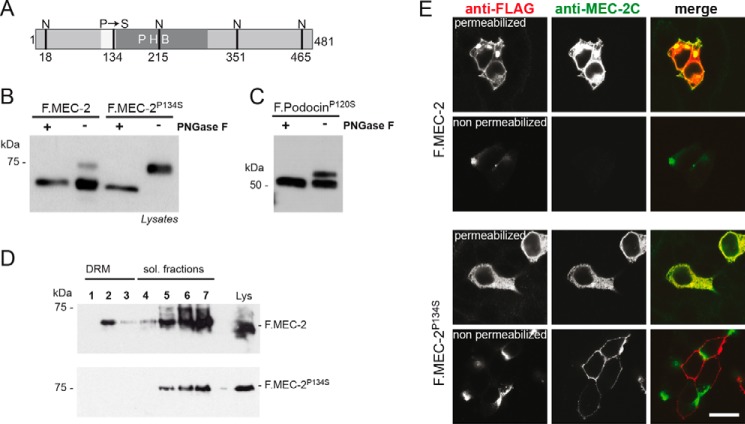
FIGURE 6.
The touch insensitivity causing mutant C. elegans protein MEC-2P134S is glycosylated and has an altered membrane topology. A, schematic of C. elegans MEC-2 depicting the hydrophobic region (white), the PHB domain (dark gray), as well as the position of the P134S mutation and the potential sites of N-glycosylation (N). B and C, FLAG-tagged, wild-type MEC-2 or MEC-2P134S was expressed in HEK 293T cells. Cell lysates were incubated with PNGase F as indicated and analyzed by Western blot analysis using anti-FLAG antibody. Wild-type MEC-2 shows a protein band of the expected molecular weight, whereas the MEC-2P134S band is shifted to a higher molecular weight. A faint band of this size is also visible with wild-type MEC-2. After treatment with PNGase F, the size shift disappears. Mouse podocinP120S shows the same behavior as mouse podocinP120L (cf. Fig. 1B). D, the association of MEC-2P134S with DRMs is disturbed. FLAG-tagged, wild-type or mutant MEC-2 was expressed in HEK 293T cells, lysed in 1% TX-100 on ice, and subjected to sucrose density gradient centrifugation. Fractions were collected from the top and analyzed by Western blot analysis. MEC-2P134S does no longer associate with DRMs. sol., soluble. E, cells were either permeabilized or non-permeabilized and exposed to anti-FLAG and anti-MEC-2 C terminus-specific antibody (anti-MEC-2C), respectively. Immunofluorescence analysis reveals that in non-permeabilized conditions, only the MEC-2P134S C terminus is accessible to antibodies. Scale bar = 20 μm.