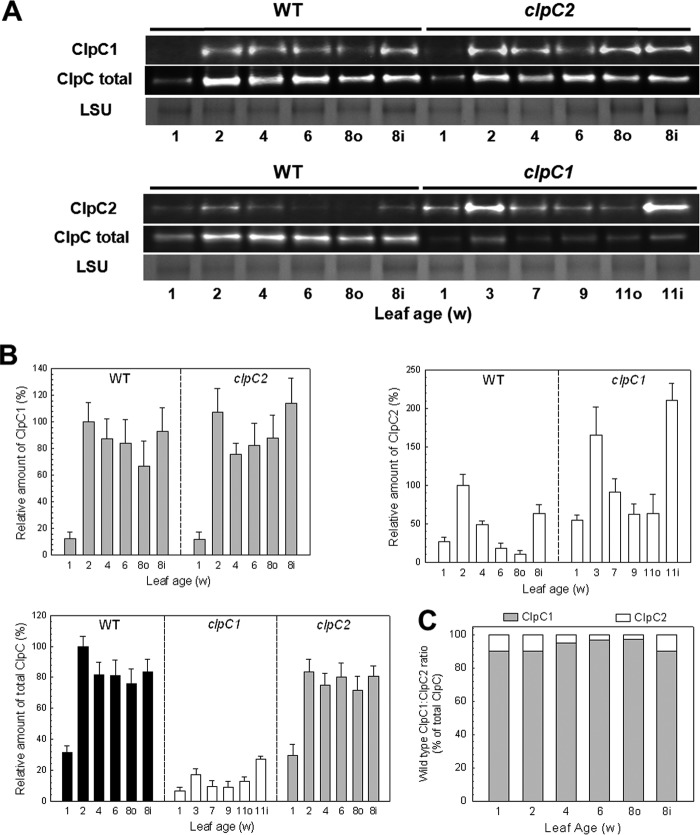
FIGURE 1.
ClpC protein abundance during vegetative growth. A, relative amounts of ClpC1, ClpC2, and total ClpC protein in cotyledons and developing leaves from Arabidopsis wild type (WT), and clpC1 and clpC2 mutants. Leaves were compared at the same developmental ages, which was 1 week old for all cotyledons and 2–8 weeks old (for WT and clpC2 mutant) or 3–11 weeks (clpC1 mutant) for developing leaves from the first rosette. Leaves from the second rosette (inner, i) were also taken at the same time as the mature leaves from the first rosette (outer, o). Total cell extracts were isolated from each sample and separated by denaturing-PAGE loaded on the basis of equal protein content. Proteins were visualized by immunoblotting using antibodies specific for ClpC1, ClpC2, or total ClpC. B, quantification of the relative amounts of ClpC1 (gray bars), ClpC2 (white bars), and total ClpC protein (black bars) in wild type Arabidopsis, and clpC1 and clpC2 mutants. Quantifications were normalized to the value from 2-week-old wild type leaves, which were set to 100%. Values shown are averages ± S.D. (n = 3). C, estimation of the relative proportions of ClpC1 and ClpC2 in wild type Arabidopsis during vegetative growth. LSU, large subunit.