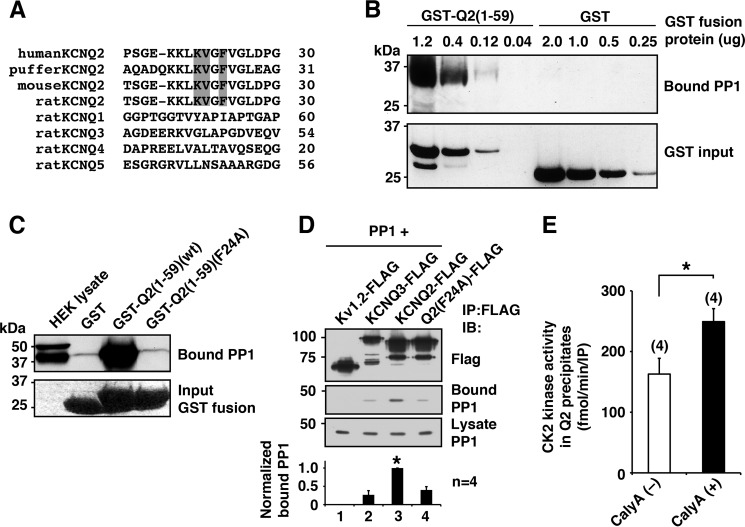
FIGURE 3.
KCNQ2 channel tethers functional PP1. A, alignment of N terminus of KCNQ channel showing conserved the KVXF motif in KCNQ2 subtype in vertebrates but not in other KCNQ subtypes. The KVXF motif is shaded. B, in vitro binding assay showing selective PP1 binding to KCNQ2 N terminus in a dose-dependent manner. C, pulldown experiments of GST-KCNQ2 N-terminal fusion proteins, GST-Q2(1–59)(WT) and GST-Q2(1–59)(F24A), showing binding of PP1 and its disruption by F24A mutation. The bottom panel shows protein staining of input proteins. D, immunoprecipitation (IP) of FLAG-tagged channels with PP1. Wild-type KCNQ2-FLAG co-precipitated a significant amount of PP1 compared with that by Kv1.2-FLAG. *, p < 0.05 by nonparametric ANOVA followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test. IB, immunoblotting. E, CK2 assay with or without a phosphatase-specific inhibitor, calyculin A (CalyA). *, p < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney test. Error bars, S.E.