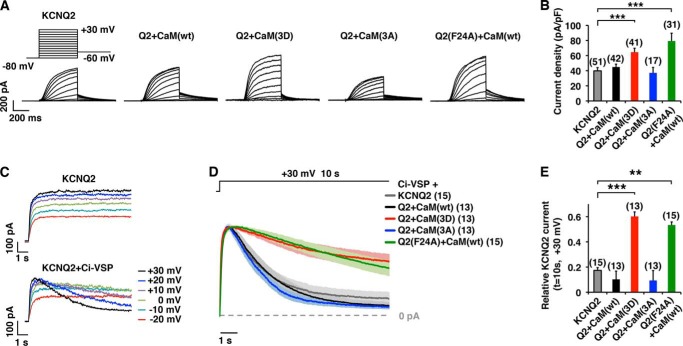
FIGURE 5.
CK2 phosphorylation mutations of CaM modified KCNQ2 current and PIP2 susceptibility. A, representative current traces of KCNQ2 currents expressed in CHO cells in the presence of CaM(WT), CaM(3D), or CaM(3A) as well as KCNQ2(F24A) + CaM(WT). At a holding potential of −80 mV, KCNQ2 currents were activated by 500-ms step depolarizations up to +30 mV, followed by −60 mV. B, KCNQ2 current density at −10 mV. ***, p < 0.001 by nonparametric ANOVA followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test. C, voltage clamp current traces showing Ci-VSP-induced rundown of KCNQ2 current. Step depolarizations (10 s), which activated noninactivating current when KCNQ2 channel was expressed alone (upper traces), showed depolarization-dependent run-down (lower traces) when co-expressed with Ci-VSP. D, average current traces ± S.E. (shaded) of scaled currents showing that the Ci-VSP-induced rundown of the KCNQ2 current was reduced by co-expression of CaM(3D) or in KCNQ2(F24A) channel. Shaded area surrounding each trace shows S.E. The data were collected from 10-s depolarization steps to +30 mV. E, histogram of relative KCNQ2 currents at t = 10 s shown in D. ***, p < 0.001 by nonparametric ANOVA followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test. Error bars show S.E.