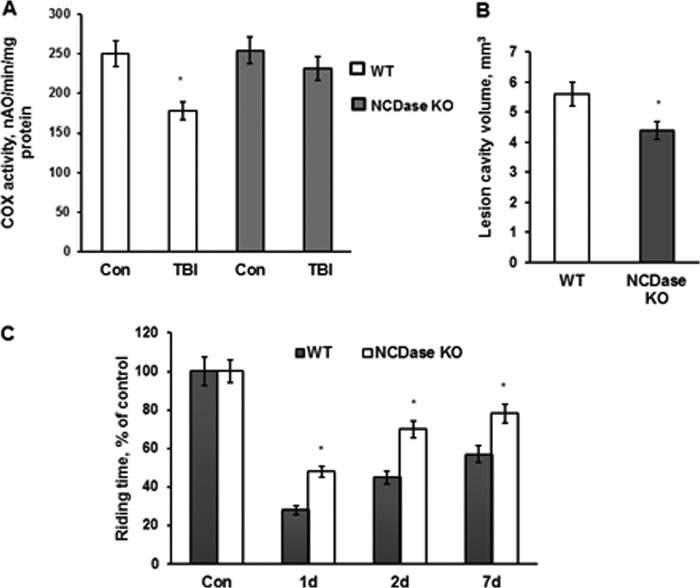
FIGURE 8.
NCDase knockdown rescued COX activity defect, attenuated brain damage, and improved sensorimotor deficit recovery after TBI. A, mitochondria were purified from the ipsilateral hemisphere of WT and NCDase KO mouse brain at day 7 post-TBI. Sham-injured animal brain was used as a control (Con). Mitochondrial COX activity was measured by recording oxygen consumption in the presence of COX substrate (1 mm ascorbate plus 250 μm TMPD), 1 μm antimycin, and 50 μm 2,4-DNP (state 3u). Data are means ± S.E. (error bars); *, p < 0.05; n = 8. B, lesion cavity volume was measured at day 28 post-TBI by staining of brain sections with 0.1% cresyl violet and image analysis as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Data are means ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05; n = 12. C, sensorimotor deficits were assessed using a standard rotarod test. Each day for 3 days prior to injury, animals were trained on the rotarod at a speed of 18 rpm in the acceleration mode (0–18 rpm/90 s). Animals were tested with the rotarod apparatus using three trials in session, with a minimum of 5 min resting between trials. Data are means ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05; n = 16.