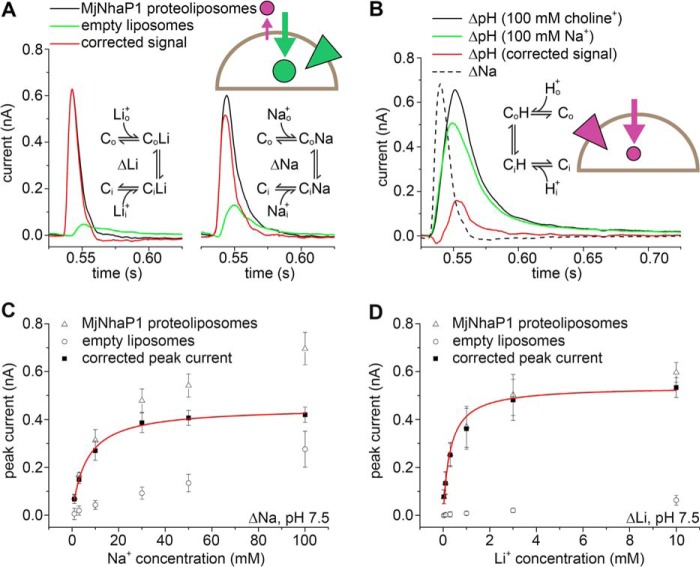
FIGURE 2.
Substrate concentration jumps performed on MjNhaP1 proteoliposomes induce a transient current. A, transient currents recorded after a 0–10 mm Li+ concentration jump (ΔLi) or a 0–50 mm Na+ concentration jump (ΔNa) at pH 7.5 on MjNhaP1 proteoliposomes or empty liposomes. Subtraction of the two signals shows the corrected transient current (in red) generated by MjNhaP1. B, transient currents recorded after a jump from pH 7.5 to pH 6.5 (ΔpH) on MjNhaP1 proteoliposomes, with either choline+ or Na+ as a background. Subtraction of the two signals shows the corrected transient current generated by MjNhaP1 (in red). For comparison the trace of a 50 mm Na+ concentration jump at pH 7.5 on the same sensor (ΔNa) is also shown. The time scale in A and B is determined by the solution exchange protocol: the valve switches at t = 0.5 s, and the activating solution reaches the SSM ∼ 35 ms later. Insets indicate the specific partial reactions involved in the particular concentration jumps. Schematics show the transport direction of H+ (purple circle and arrow) and Na+ (green circle and arrow), as well as the direction of the Na+ (green triangle) or H+ (purple triangle) gradients. C and D, substrate dependence of transient currents at pH 7.5. Dependence of the peak currents was recorded for concentration jumps of Na+ (ΔNa, C) or Li+ (ΔLi, D) at pH 7.5. Peak currents recorded on MjNhaP1 proteoliposomes could be corrected for solution exchange effects by subtraction of peak currents recorded on empty liposomes. Red lines are hyperbolic fits of the corrected peak currents. Fit parameters are given in Table 1. Error bars, S.D.