FIGURE 11.
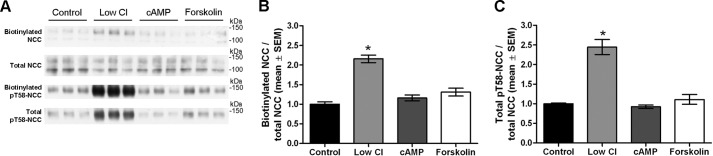
Hypotonic low chloride treatment of MDCKI-NCC cells increases NCC membrane abundance and Thr-58 phosphorylation. A, representative Western blot of samples from an apical surface biotinylation experiment of MDCKI-NCC cells grown on semi-permeable supports and treated with hypotonic low chloride, 25 μm forskolin, 50 μm (Sp)-cAMP, or control conditions. Biotinylated and total pools were blotted for total NCC and Thr(P)-58NCC. B, semi-quantitative assessment of apical membrane NCC abundance. Hypotonic low chloride conditions significantly increased surface levels of NCC. C, semi-quantitative assessment of total Thr(P)-58NCC levels. Thr(P)-58NCC abundance is significantly increased with hypotonic low chloride. Data are means ± S.E. (n = 6). * represents significant change compared with control treatment.
