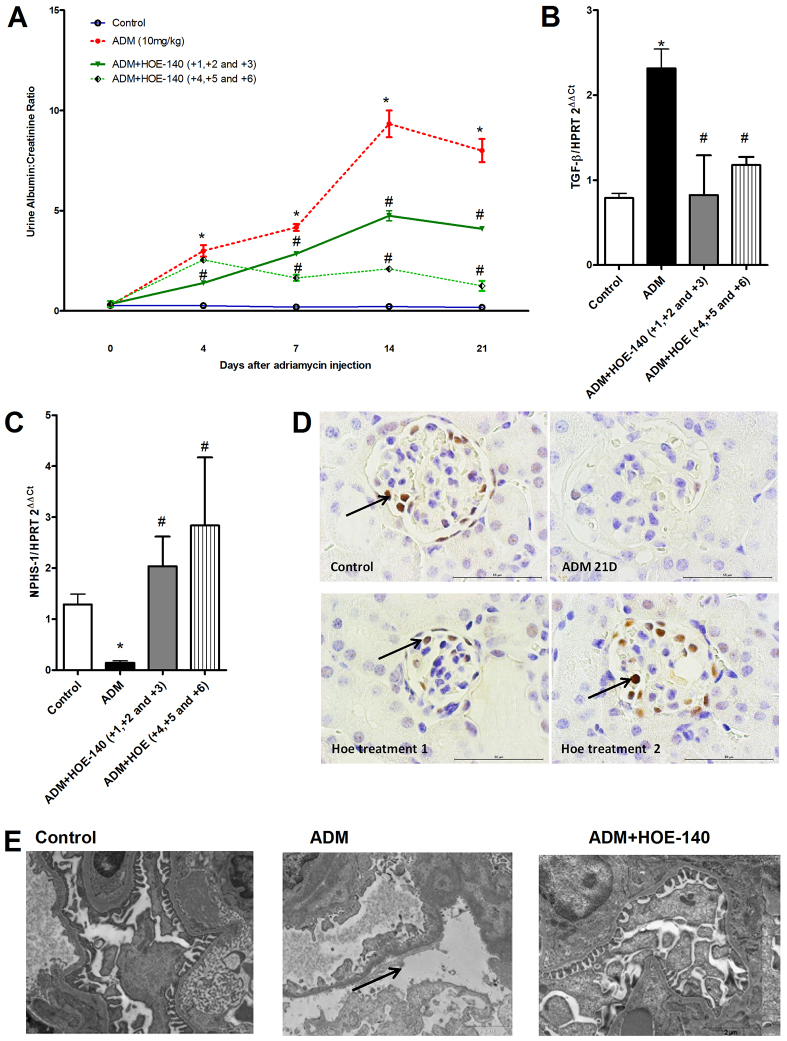
Fig. 5.
Treatment with HOE-140 induced sustained protection of mice from FSGS development. The balb/c mice were divided into two groups. In the first group, the mice were treated with HOE-140 at days 1, 2 and 3 after the injection of Adriamycin (ADM) (early treatment), and in the second group, the mice were treated with HOE-140 at days 4, 5 and 6 after the injection of ADM (delayed treatment). At the end of the two protocols, the mice were killed at day 21. Treatment with HOE-140, in both groups, protected mice from albuminuria (A). HOE-140 also prevented the upregulation of TGF-β mRNA (B) and prevented the downregulation of nephrin (NPHS-1) (C). Expression of the mRNAs were normalized to that of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT). HOE-140 also prevented the downregulation of the WT-1 staining that was induced by ADM injection, as observed by immunohistochemistry (D). ADM 21D, day 21 after injection of ADM; HOE treatment 1, early treatment; HOE treatment 2, delayed treatment. Black arrows indicate WT-1-positive cells. Scale bars: 50 μm. (E) By using electron microscopy analysis, we observed that HOE-140 prevented the podocyte foot process effacement that was induced by Adriamycin injection. Black arrow indicates podocyte effacement. *P<0.05 compared with that of control mice, #P<0.05 compared with that of mice treated with only ADM. Five animals were used per study group.