Fig. 6.
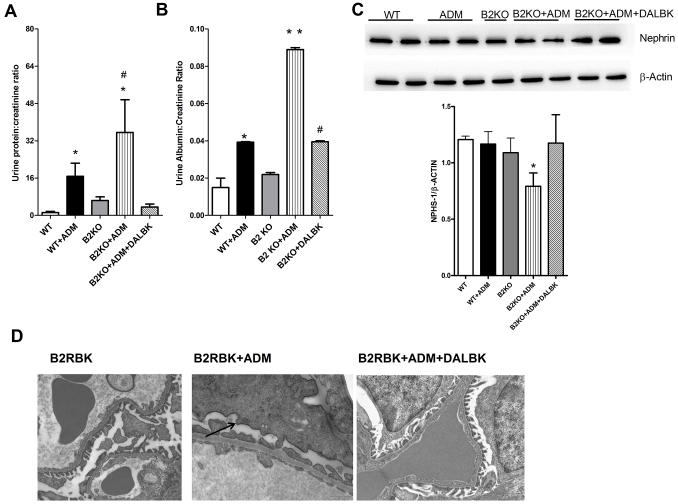
The lack of B2RBK receptor exacerbates Adriamycin nephropathy. C57-black-background mice were killed at day 7 after Adriamycin (ADM) injection. The lack of B2RBK (B2KO) exacerbates the ADM-induced proteinuria (A) and albuminuria (B), and these effects were downregulated by treatment with DALBK. ADM injection downregulated nephrin (NPHS-1) protein expression in B2RBK-knockout mice, and this downregulation was prevented by DALBK (C), as shown by western blotting (upper panel). The lower panel shows the quantification of the western blot analyses, where the level of nephrin was normalized to that of β-actin for each sample. (D) We observed that DALBK protects B2RBK-knockout mice from podocyte foot process effacement, by using electron microscopy. The black arrow indicates podocyte effacement. *P<0.05 compared with that of control mice, **P<0.05 vs all other groups, #P<0.05 compared with that of mice treated with only ADM. Five animals were used per study group.