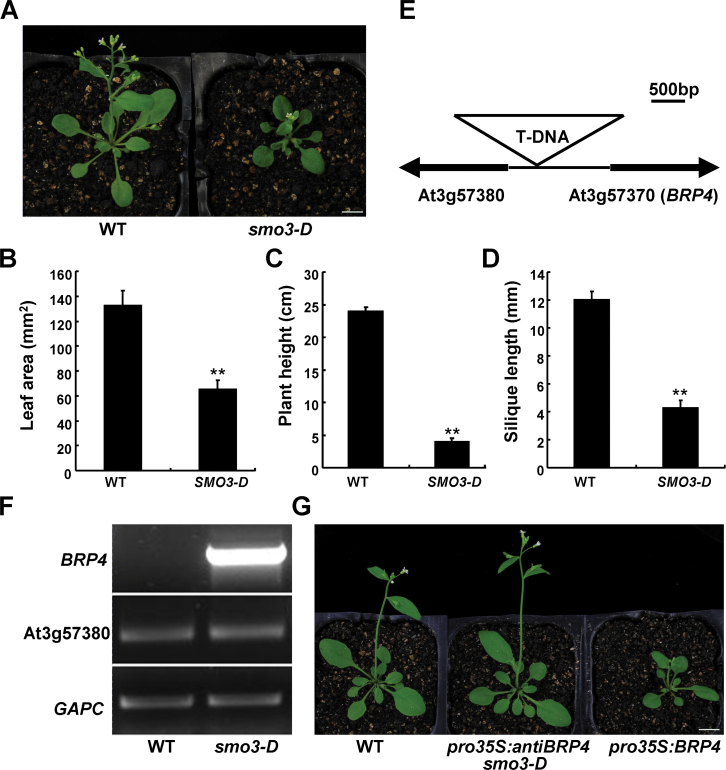
Fig. 1.
Ectopic expression of BRP4 affects aerial organ development. (A) Morphology of 23-d-old WT, left) and smo3-D plants (right). Bar, 1cm. (B) The area of fully expanded fifth leaves of WT and smo3-D plants. At least six leaves from each genotype were used to determine areas, and the data are shown as means±standard deviation (SD) (Student’s t-test, **P<0.01). (C, D) Plant height (C) and silique length (D) of WT and smo3-D plants. Fifty-day-old plants were used for determination of plant height and silique length; the data were from 15 plants of each genotype and data are presented as means±SD (Student’s t-test, **P<0.01). (E) Schematic illustration of the genomic region at the BRP4 locus in smo3-D. The coding regions of both At3g57370 (BRP4) and At3g57380 are indicated as black arrows, and the intermediate genomic sequence is indicated as a black line. T-DNA was inserted in the promoter region of BRP4, 1014bp upstream of ATG. (F) RT-PCR analysis of BRP4 and At3g57380 expression in WT and smo3-D plants. (G) Morphology of 3-week-old transgenic pro35S:BRP4 plants and smo3-D carrying a pro35S:antiBRP4 construct. Bar, 1cm.