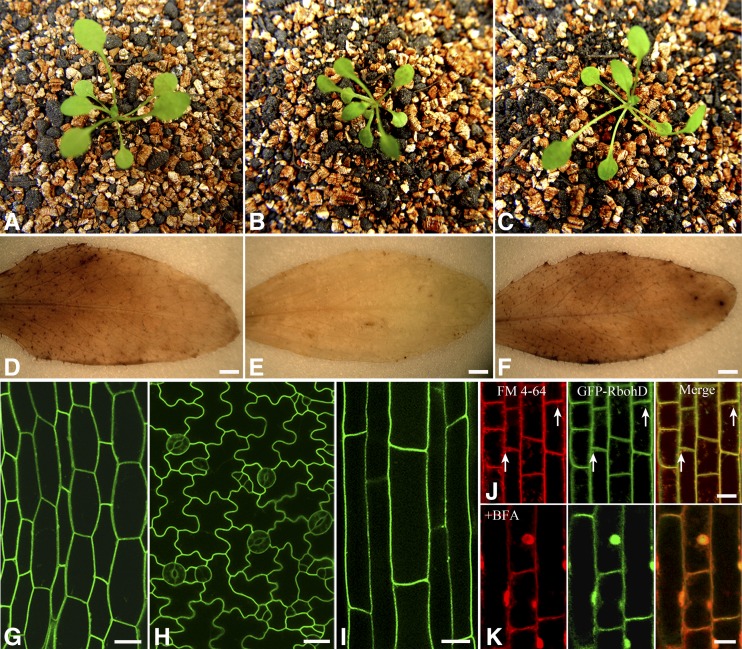
Figure 1.
Distribution and Localization of GFP-RbohD in Arabidopsis Seedlings.
(A) to (C) Phenotypes of wild-type (A), rbohD (B), and pRbohD:GFP-RbohD transgenic seedlings in the rbohD background (C).
(D) to (F) H2O2 production in leaves of wild-type (D), rbohD (E), and pRbohD:GFP-RbohD transgenic seedlings in the rbohD background (F) was visualized using 3,3′-diaminobenzidine. Bars = 1 mm.
(G) to (I) Confocal images of the expression of GFP-RbohD in Arabidopsis seedlings. Micrographs show that GFP-RbohD was localized mainly at the plasma membrane in Arabidopsis hypocotyls (G), leaf epidermal cells (H), and root cells (I). Bars = 20 μm.
(J) Roots of Arabidopsis seedlings were stained with endocytic tracer FM4-64 (3 μM) and then observed after incubation for 10 min. In control cells, colocalization of GFP-RbohD and FM4-64 was observed at the plasma membrane and the intracellular structure (white arrow). FM4-64 labeling (red), GFP-RbohD (green), merged channels (yellow).
(K) When roots were pretreated with BFA (50 μM) for 1 h and then incubated with 50 μM BFA and 5 μM FM4-64 for 30 min, GFP-RbohD colocalized with FM4-64 in the BFA compartment. For all analyses, the results shown are representative of >15 independent samples. Bars = 10 μm (J) and (K).