Figure 2.
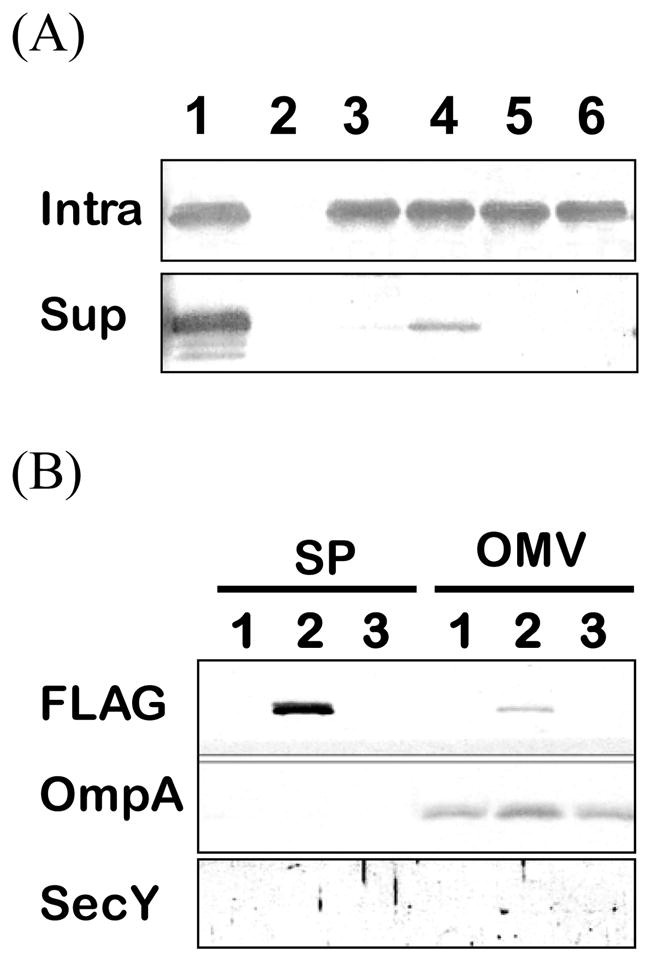
HH domain is important for B. subtilis enolase secretion in E. coli. (A) Samples of soluble cell lysates (Intra) and supernatant (Sup) were analyzed by immunoblots with EnoBs antibodies under conditions E. coli enolase was not detected. Lane 1, wild-type EnoBs; lane 2, DH5α (pDG148) as a control for non-cross reaction with E. coli intrinsic enolase; lane 3, EMR [1]; lane 4, AIL→GGG; lane 5, GVS→GGG; lane 6, MAC→GGG. (B) Immunoblot analyses of extracellular supernatant (SP) and spontaneously released outer membrane vesicles (OMV) using the specific antisera as indicated: FLAG is the marker for EnoBs; OmpA is a marker for outer membranes; and SecY is a marker for cytoplasmic membranes. Lane 1, DH5α; lane 2, EnoFLAG (pEnoFLAG); lane 3, VS→GG (pVSFLAG).
