Figure 1. RAS signalling pathways in mammalian cells.
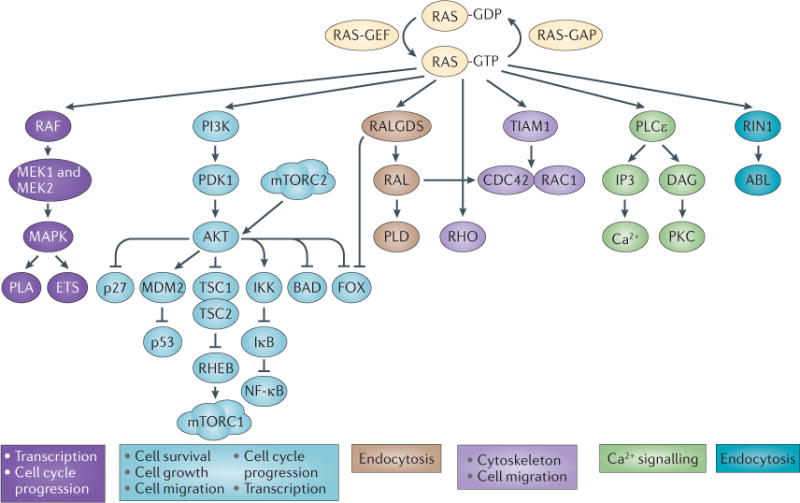
Active (farnesylated, membrane-bound and GTP-bound) RAS modulates a number of signalling pathways. Oncogenic RAS mutations tend to lock RAS in its GTP-bound state, resulting in constitutive RAS signalling. The major RAS effector pathways are shown. The two best-studied pathways that are activated by RAS are the RAF–MEK–MAPK signalling cascade and the PI3K–AKT pathway. The RAF–MEK–MAPK pathway ultimately activates the ETS family of transcription factors, which induce multiple genes that promote cell cycle progression and cell migration. Likewise, AKT phosphorylates multiple cellular proteins, leading to the inhibition of several tumour suppressors (such as p27, p53, tuberous sclerosis 1 (TSC1), TSC2 and BCL-2 antagonist of cell death (BAD)) or leading to the activation of several oncogene products. RAS also activates other small GTPases such as RALA and RALB, which have recently been shown to mediate RAS transformation in human pancreatic tumours, for example. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors (FTIs) were originally developed to block the function of RAS. However, as numerous studies in vitro and in vivo have shown, their antitumour activity is not correlated to the mutation status of KRAS isoforms. This suggests that the antitumour activity of FTIs relies on blocking the activity of other prenylated proteins. However, the inhibition of RAS protein function may still be important, particularly for tumours with mutant HRAS and tumours addicted to wild-type RAS. CDC42, cell division cycle 42; DAG, diacylglycerol; FOX, forkhead transcription factor; GAP, GTPase-activating protein; GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor; IKK, IκB kinase; IP3, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate; mTORC, mTOR complex; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; PKC, protein kinase C; PLA, phospholipase A; PLCε, phospholipase Cε; PLD, phospholipase D; RALGDS, RAL guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator; RHEB, RAS homologue enriched in brain; RIN1, RAS and RAB interactor 1; TIAM1, T cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 1.
