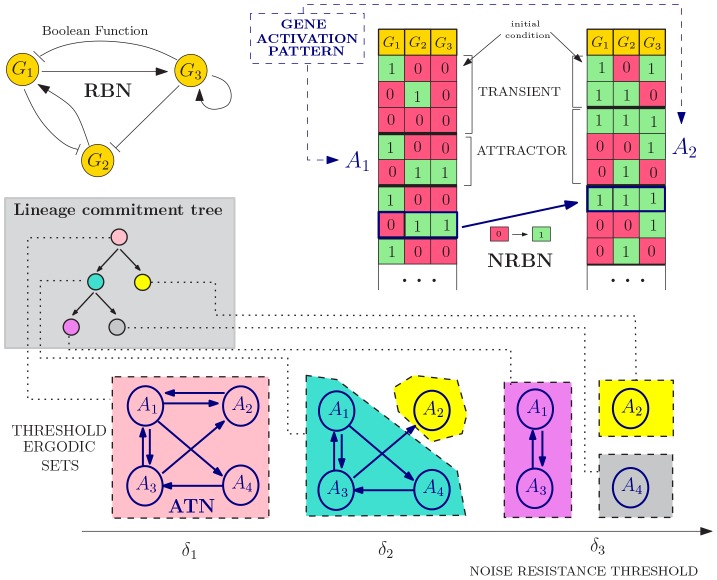
Figure 3. Noise-induced stochastic differentiation.
An example NRBN with  genes is shown, boolean functions are omitted. Two initial genetic configurations yield two gene activation patterns: attractors
genes is shown, boolean functions are omitted. Two initial genetic configurations yield two gene activation patterns: attractors 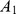 and
and 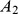 , whose noise-resistance is evaluated via flipping different nodes in different phases and leading to an Attractors Transition Matrix. The emerging lineage commitment tree consists of
, whose noise-resistance is evaluated via flipping different nodes in different phases and leading to an Attractors Transition Matrix. The emerging lineage commitment tree consists of  cell types (one for each Threshold Ergodic Set for the
cell types (one for each Threshold Ergodic Set for the  noise thresholds
noise thresholds 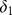 ,
, 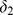 and
and 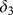 ). The differentiation level corresponds to the noise-resistance, e.g., the toti-/multi-potent stem-alike cell type (pink) roams among all possible gene activation patterns, the grey/yellow cell types are fully differentiated cells. This model of differentiation has branches, i.e. a newborn pink cell has probability of differentiating in a green or yellow cell proportional to the properties of the attractors (see Figure 4).
). The differentiation level corresponds to the noise-resistance, e.g., the toti-/multi-potent stem-alike cell type (pink) roams among all possible gene activation patterns, the grey/yellow cell types are fully differentiated cells. This model of differentiation has branches, i.e. a newborn pink cell has probability of differentiating in a green or yellow cell proportional to the properties of the attractors (see Figure 4).