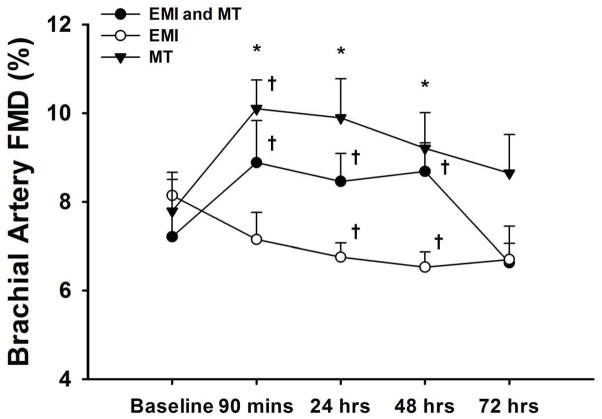
Figure 1.
The effects of exertion-induced muscle injury (EMI) and/or massage therapy (MT) on brachial artery flow-mediated dilation (FMD) in sedentary adults at five time points during the study period. *Significant differences observed in EMI only group versus MT only group (p < 0.05). †Significant within group differences observed from baseline (p < 0.05).