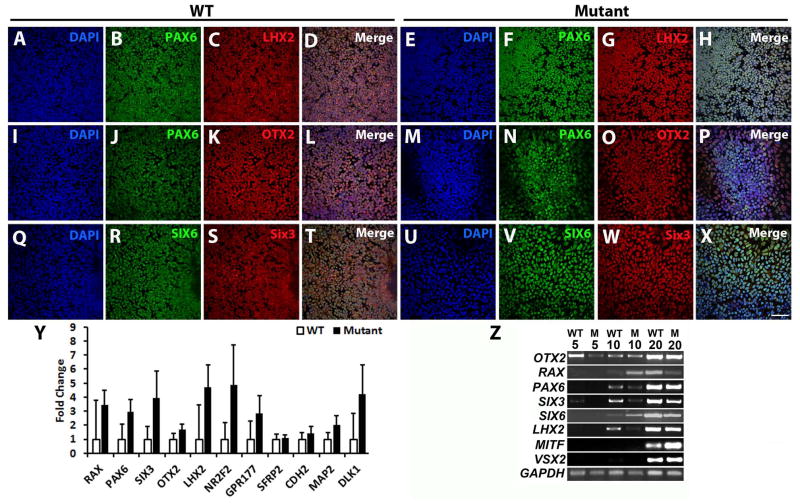
Figure 1. The (R200Q)VSX2 mutation does not affect anterior neuroectoderm/eye field specification in differentiating hiPSCs.
Representative immunocytochemical analysis of WT (A–D, I–L, Q–T) and (R200Q)VSX2 mutant (E–H, M–P, U–X) hiPSC cultures at day 10 of differentiation. Cell nuclei were identified with DAPI (A, E, I, M, Q, U). In both WT and mutant cultures, tightly packed neural colonies uniformly expressed the eye field transcription factors PAX6 (WT: B, J and mutant: F, N); LHX2 (WT: C and mutant: G); OTX2 (WT: K and mutant: O); SIX6 (WT: R and mutant: V); and SIX3 (WT: S and mutant: W). Merged images are shown in panels D, L, and T (WT) and H, P, and X (mutant). Scale bar = 50 μm. (Y) qRT-PCR analysis revealed similar expression levels of key eye field genes in WT and mutant cultures at day 10 (n=3 separate hiPSC lines for both groups with 3 biological replicates per line). (Z) Representative RT-PCR analysis demonstrated upregulation of critical eye field and optic vesicle transcription factors in WT and mutant (M) cultures over time.