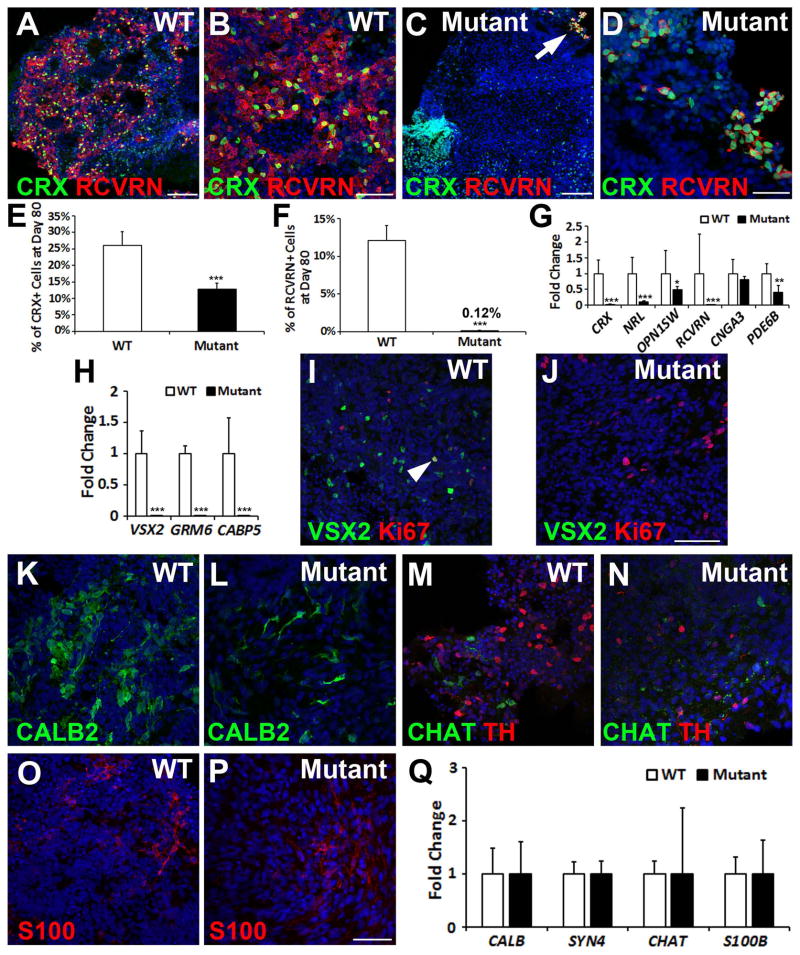
Figure 4. The (R200Q)VSX2 mutation delays photoreceptor maturation and prevents bipolar cell differentiation.
(A–D) At day 80, numerous CRX+ cells co-expressed RCVRN in WT hiPSC-OVs (A, B), whereas CRX+ nuclei in mutant hiPSC-OVs rarely co-expressed RCVRN (C, D) (arrow in panel C is shown at a higher magnification in panel D). Scale bars = 100 μm (A, C); 50 μm (B, D). (E) Stereological counts confirmed a reduction in the percentage of CRX+ nuclei in mutant hiPSC-OVs at day 80. (F) Also at day 80, mutant hiPSC-OVs showed a ~100-fold reduction in the percentage of RCVRN+ nuclei relative to WT hiPSC-OVs. Of note, all pigmented hiPSC-OVs were excluded from these studies. (G) qRT-PCR analysis revealed reduced levels of expression for most photoreceptor genes in mutant hiPSC-OVs compared to WT hiPSC-OVs at day 80. (H) The bipolar cell genes VSX2, GRM6, and CABP5 were not expressed in mutant hiPSC-OVs, as shown by qRT-PCR. (I) Immunocytochemical analysis demonstrated persistence of VSX2+ cells in WT hiPSC-OVs at day 80, most of which were Ki-67 negative, indicative of bipolar cell differentiation. However, occasional VSX2+/Ki-67+ NRPCs were also present (arrowhead). (J) In contrast, VSX2 was no longer expressed in mutant hiPSC-OVs at day 80, confirming a lack of bipolar cell generation. Scale bar in panel J = 100 μm (also applies to panel I). (K–P) Both WT and mutant hiPSC-OVs produced neural retina cell types other than bipolar cells, including CALB2+ neurons (K,L), CHAT+ and TH+ amacrine cells (M,N), and S100+ glia (O,P). Scale bar in panel P = 50 μm (also applies to K–O). (Q) qRT-PCR analysis comparing neural retina gene expression in WT vs. mutant hiPSC-OVs at day 80. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.