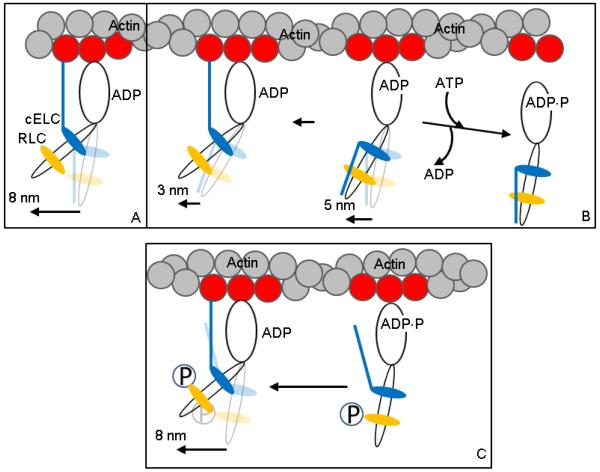
Figure 6.
Hypothetical 3 step-size mechanism for βMys moving actin in vitro and its modification by RLC S15 phosphorylation. Panels A and B depict the unphosphorylated βMys species and Panel C the phosphorylated species. Panel A is the full lever-arm swing of 8 nm with actin binding of the cELC N-terminus. Panel B shows the 5 nm step followed by detachment from actin (towards right) or an unlikely event when lingering ADP causes a subsequent 3 nm step (towards left). The actin binding N-terminus peptide of cELC is frequently constrained to a position unfavorable for its attachment to actin. Panel C shows the actin binding N-terminus peptide of cELC pre-positioned to interact with actin due to repulsion of the peptide by phosphate (P) at S15 of pRLC. This conformation favors the 8 nm step.