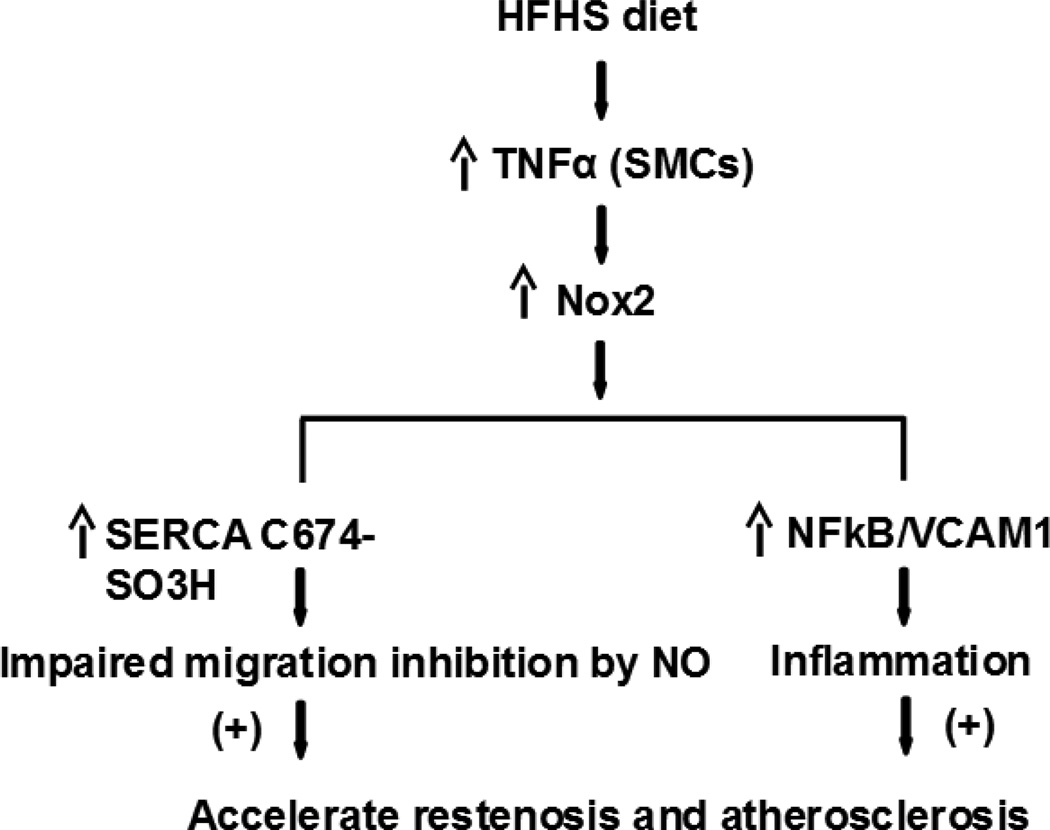
Figure 6. Scheme of the potential mechanisms by which HFHSD contributes to cardiovascular diseases.
HFHSD-induced TNFα stimulates Nox2 and inflammation, leading to SERCA oxidation, decreased NO bioactivity, and increased SMC migration and macrophage adhesion to SMC, which can all contribute to vessel restenosis and atherosclerosis in settings of obesity.