Figure 3. Knockdown of FKBP1b or treatment with rapamycin (Rap) increased Ca2+ channel current in cultured hippocampal neurons.
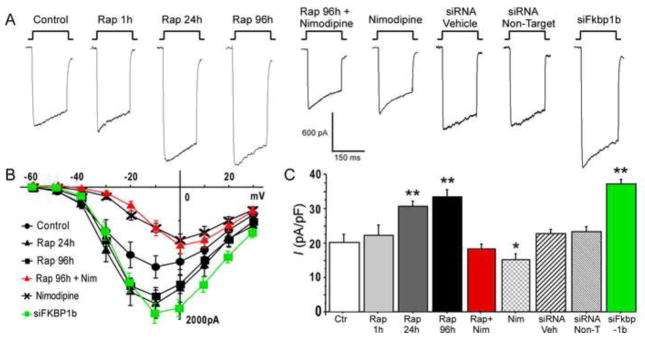
A, Representative whole-cell patch-clamp current traces from each experimental condition; B, Mean current/voltage (I/V) relationships for 6 of the 9 experimental conditions. The I–V curves for Rap 1h, siRNA Veh and siRNA Non-Target were not different from the control condition and are omitted for illustrative clarity. Exposure to siFkbp1b for 96 h or to rapamycin for 24/96 h induced enhancement of VGCC current. Treatment with siFkbp1b or with rapamycin altered the amplitude but not the voltage dependence of Ca2+ current, whereas nimodipine (Nim) shifted peak current to more positive voltage; C, Means +/− S.E.M. of peak Ca2+ current density for the 9 conditions. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the control condition (* p < 0.05 and **p < 0.0001). n = control (18), Rap 1h (4), Rap 24h (20), Rap 96h (20), Rap + Nim (10), Nim (12), siRNA Veh (23), siRNA Non-Target (19), siFkbp1b (23). (From Gant et al., 2011)
