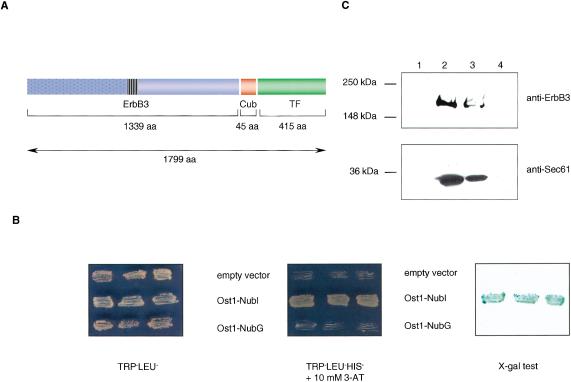
Figure 3.
(A) The structure of the ErbB3-Cub-TF bait protein used in this study. Like other members of the ErbB family, ErbB3 is a type I transmembrane protein consisting of an extracellular ligand binding domain (blue dotted box), a single membrane-spanning region (striped box), and a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase domain (blue open box). The ErbB3 bait was fused to Cub (red box), followed by an artificial transcription factor (TF; green box). The number of amino acids of ErbB3, Cub, and TF portions are indicated. (B) Growth of yeast cells expressing ErbB3-Cub-TF bait with various Nub-fusions on agar plates lacking tryptophan and leucine (left), and tryptophan, leucine, and histidine containing 10 mM 3-aminotriazole (3-AT; middle). The L40 yeast reporter strain was cotransformed with the ErbB3-Cub-TF bait and indicated prey plasmids, and three independent colonies were grown on Leu-Trp- and Leu-Trp-His-selective plates prior to assessment of β-galactosidase activity using X-gal filter test (right). (C) ErbB3 is localized within the yeast membrane. Cytosolic (lanes 1 and 3) and membrane (lanes 2 and 4) fractions of yeast cells expressing the ErbB3-Cub-TF bait were subjected to SDS-PAGE. The insoluble fraction (lane 2) was treated with 1% Triton X-100 to solubilize the proteins, and centrifuged to separate the soluble (lane 3) from insoluble proteins (lane 4). The ErbB3-Cub-TF bait and a control endogenous yeast membrane protein Sec61p were detected by immunoblot analysis using a mouse monoclonal anti-ErbB3 antibody (upper panel), and an anti-Sec61 polyclonal antibody (lower panel). The positions of molecular markers are indicated.