Figure 9.
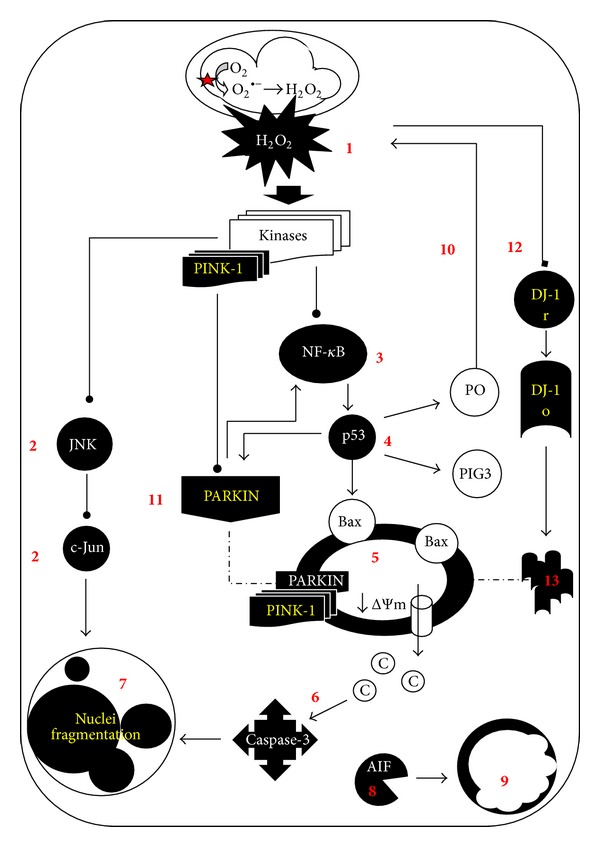
Schematic model of the major molecular events by which rotenone provokes apoptosis in Jurkat cells under different glucose conditions. Rotenone inhibits complex-I (NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase) ensuing overproduction of superoxide anion radicals (O2 ∙−) which dismutate enzymatically (by superoxide dismutase, SOD) or nonenzymatically into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). This last compound freely diffuses through mitochondrial membranes to cellular cytoplasm (1). H2O2 may in turn activate one or several kinases (e.g., the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1, MEKK1; spleen tyrosine kinase, Syk; apoptosis signal regulating kinase-1, ASK) which can directly or indirectly activate both JNK/c-Jun (2) and NF-κB (3) via phosphorylation of the IκBα (i.e., the repressor of NF-κB). Once NF-κB is active, it translocates into the nucleus and transcribes p53 protein (4). In turn, p53 transcribes proapoptotic proteins (e.g., Bax) which are able to permeabilize mitochondria (5), thus promoting the activation of caspase-3 (6), which signals DNA fragmentation ((7), stage II nuclei fragmentation), and chromatin fragmentation ((9), stage I nuclei fragmentation) as a result of the apoptotic-inducer factor (AIF) protein action (8). Additionally, p53 can establish two independent but complementary vicious cycles. It can transcribe pro-oxidant proteins (e.g., p53-induced gene-3 (PIG3), proline oxidase (PO), (10), which generate more H2O2 (1) amplifying the initial H2O2 > kinases > NF-κB > p53 cell death signaling. p53 can also transcribe Parkin protein (11), which is phosphorylated by the autophosphorylated PINK-1 protein, to further activate NF-κB (3), thus amplifying the NF-κB > p53 > Parkin death axis. The overproduction of H2O2 also causes DJ-1 (12) oxidation (DJ-1 o) of Cysteine106 residue into cysteine sulfonate (Cys106-SO3 −). This chemical reaction might change the structural conformation of DJ-1 into protein aggregates (13). However, when cells are cultured in high glucose concentration (e.g., 55 mM glucose) in presence of ROT, they are able to properly mount an antioxidant response (e.g., probably via pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) to increase GSH by NADPH generation). Hence, functional mitochondria and normal nuclei morphology are preserved.
