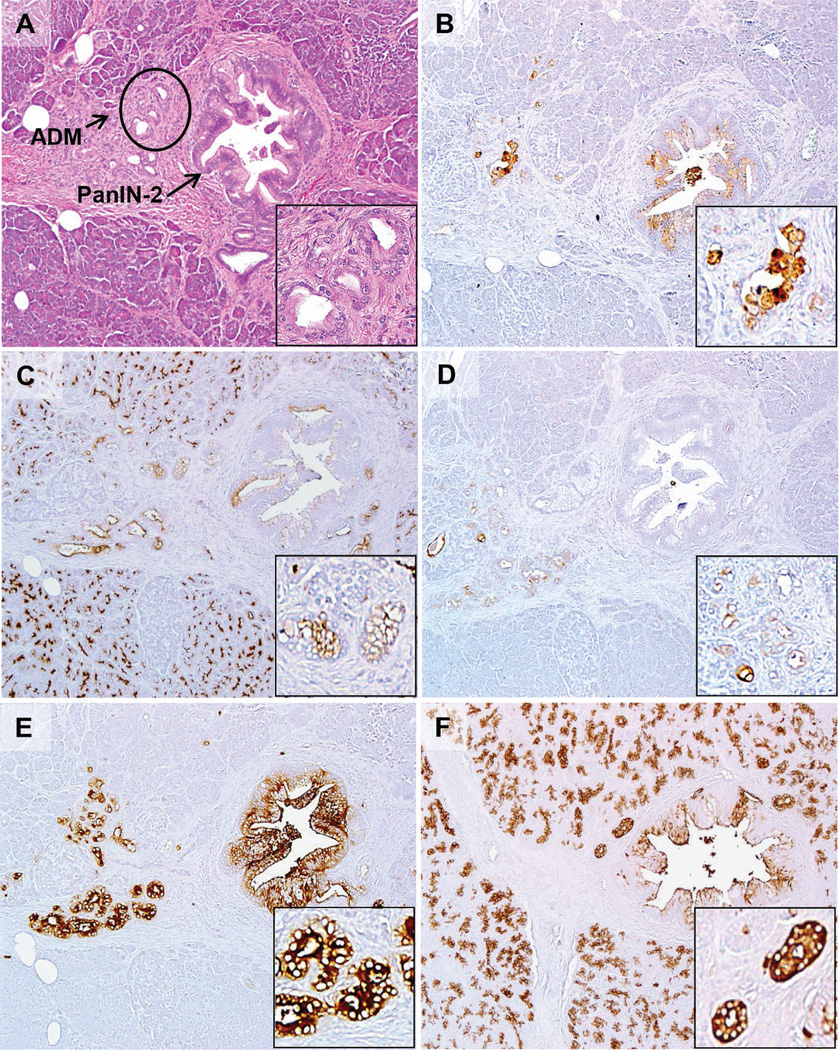
Figure 2.
Expression of the PAM4 biomarker, MUC1, MUC4, CEACAM5/6, and CA19-9 in a pancreatic intraepithelial neoplastic (PanIN-2) lesion identified within a case of chronic pancreatitis. A, The hematoxylin-eosin section shows the PanIN-2 arising within a background of chronic pancreatitis with partial loss of acinar cells, some fibrosis, and acinar ductal metaplasia (ADM). Arrows are pointed at PanIN-associated ADM, with the circled ADM shown at higher magnification in the inset. B, PAM4 labeled the PanIN lesion along with focal chronic pancreatitis-associated ADM. C, MUC1 was expressed by the PanIN lesion, as well as associated ADM and acinar cells. D, MUC4 was present within associated ADM, but not the PanIN lesion in this case. E, CEACAM5/6 showed strong labeling of the PanIN lesion, ADM, and inflammatory cells. F, CA19-9 showed moderate labeling of the PanIN lesion, but also labeled the acinar cells, duct, and ADM (original magnifications ×40 [A–F] and ×200 [A–F insets]).