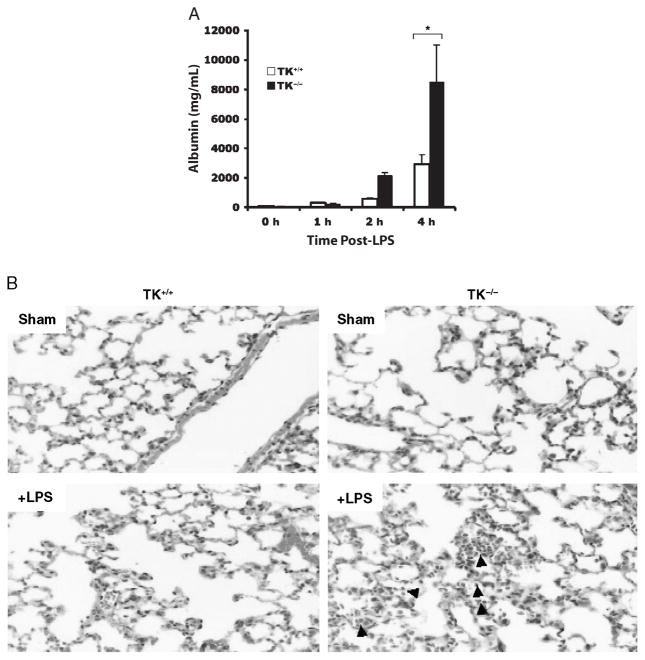
Fig. 1. Lung injury in wild-type (TK+/+) and Ron tyrosine kinase-deficient (TK−/−) mice after intranasal administration of LPS.
A, The levels of albumin were measured in BAL fluids as an index for vascular leakage. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM with n = 3 to 5 mice per group. *P < 0.05 compared with TK+/+ treated mice. B, Histological analysis of stained lung tissues obtained from TK+/+ and TK−/− mice treated with saline (sham) or LPS. Sections from each lung of the TK−/− mice exhibited acute pneumonitis defined by inflammatory cells in the airspaces compared with the TK+/+ mice. Arrows point to inflammatory cells in the airspaces of the TK−/− lung section.