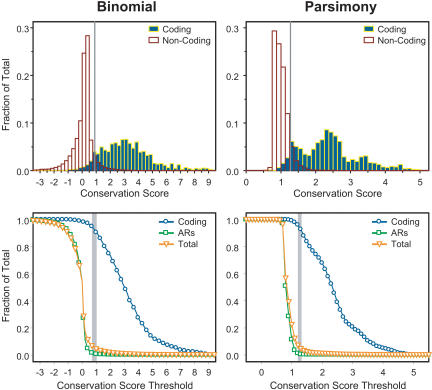
Figure 1.
Discrimination of different types of sequence using conservation scores calculated by the binomial- (left) and parsimony- (right) based methods. The top two histograms depict the distribution of conservation scores calculated for coding (blue outlined in yellow) and non-coding (white outlined in red) sequence by each method. Note that the distributions are represented as a fraction of the total sequence in each annotated category and that only 1.1% of the sequence in the analyzed region represents coding sequence. The vertical lines indicate the conservation score thresholds used for defining MCSs (see text). The bottom two graphs show the detection of different types of sequence at increasing conservation score thresholds. The fraction of sequence in each annotated category (coding, ARs, and total) that exceeded the indicated conservation score threshold is plotted. The vertical bars (shaded in grey) reflect the small range of conservation score thresholds that optimally results in the detection of nearly all coding sequence along with a minimum amount of the total sequence (4% to 7%).