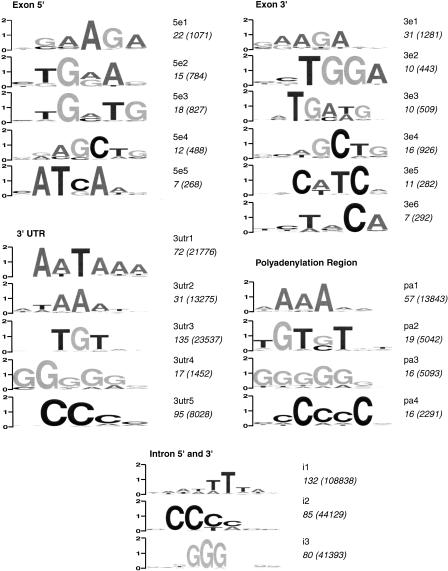
Figure 2.
Overrepresented motifs, corresponding to putative regulatory elements in human genes. Each sequence logo represents the consensus sequence of a family of regulatory elements determined by clustering and alignment of sequences within various regulatory regions. The vertical scale (bits) corresponds to the information content and degree of conservation. The name of each family appears to the right of the pictogram (e.g., 5e1 is the first exonic family in the 5′ exonic region). The number of distinct, overrepresented hexamer sequences contributing to the consensus alignment is shown under the name. The total number of such motifs within the human genes tested is shown in parentheses. Note that the total number of motifs includes overlapping sequences and is not equal to the number of regulatory elements present in the genome. It may be interpreted, however, as the relative importance of each family of putative regulatory elements.