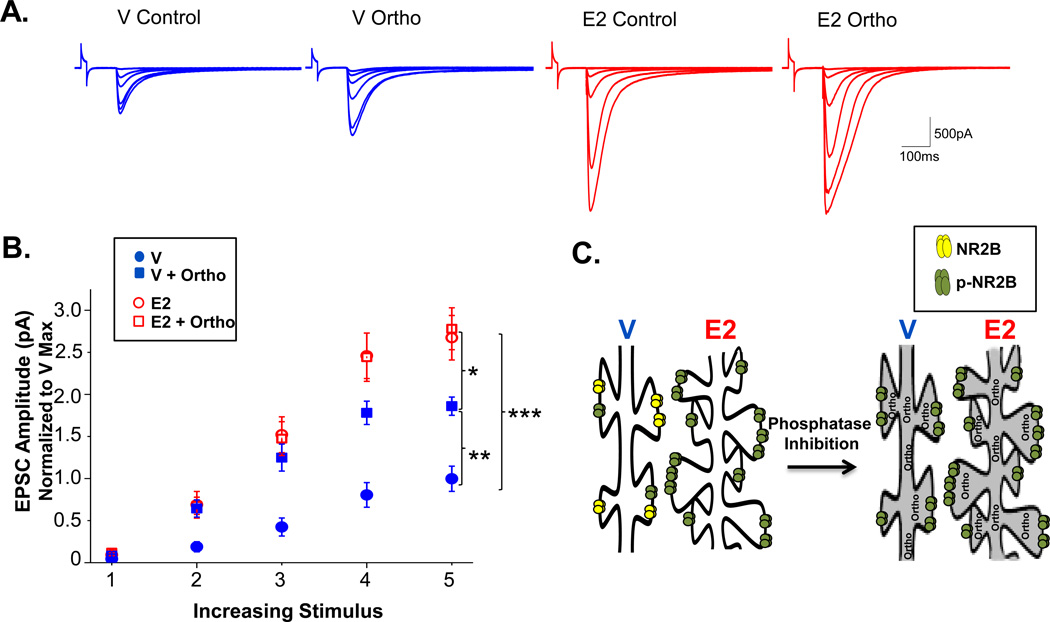
Figure 3. E2 enhances both phosphorylation of NR2B-containing NMDARs and total NR2B-containing NMDARs in the synapse.
A. Representative traces for each group with over-layed responses for each stimulus intensity. B. Normalized whole-cell recordings of evoked NMDAR EPSCs at increasing stimulus intensities from V-treated animals with (closed squares) or without (closed circles) orthovanadate in the pipet solution and E2-treated animals with (open squares) or without (open circles) orthovanadate. The maximum evoked NMDAR current measured in cells from E2-treated animals is significantly increased above that measured in cells from V-treated rats. Orthovanadate has no effect in cells from E2-treated animals, but significantly enhances the maximum current elicited in cells from V-treated animals. ***p<0.0005, ** p<0.005, *p<0.05. C. Cartoon model illustrating differences in NMDAR receptor density and subunit phosphorylation in CA1 pyramidal cells from E2-treated versus control rats, and the lack of effect of orthovanadate in E2 versus control cells due to E2-induced saturation of subunit phosphorylation.