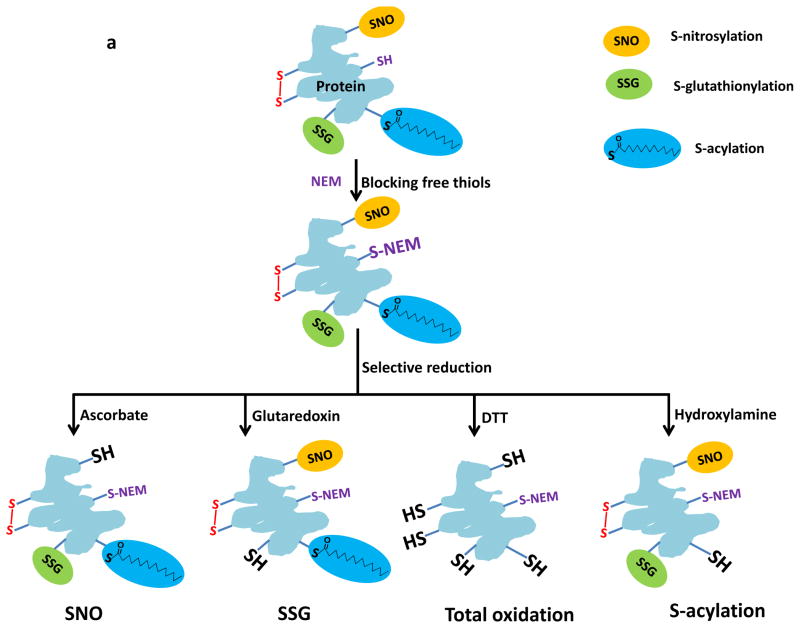
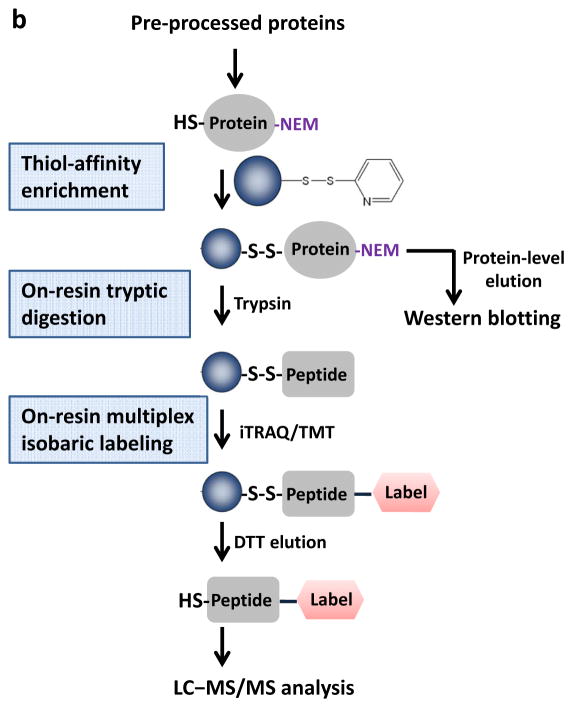
Figure 1.
Schematic of the pre-processing and enrichment strategy for different reversible cysteine modifications. (a) Sample pre-processing strategies for different types of reversible cysteine modifications. The free thiols are initially blocked by alkylation and the different types of modified cysteines are selectively reduced to free thiols by using individual sets of reagents. Note that the term “total oxidation” is not exact as S-acylation is not a form of oxidation; however, the level of S-acylation is negligible compared to other forms of redox modifications. Also note that the breaking of S-acylation thioester bonds by DTT may not be effective since the reaction between DTT and thioesters is a much slower reaction compared to hydroxylamine. (b) Enrichment method for quantitative analysis of reversible cysteine modifications. After preprocessing, the free thiols derived from modified cysteines are captured by Thiopropyl Sepharose resin. Enriched proteins can be directly eluted for gel electrophoresis. On-resin digestion and on-resin isobaric labeling are performed for quantitative LC MS/MS analysis.