Fig. 4.
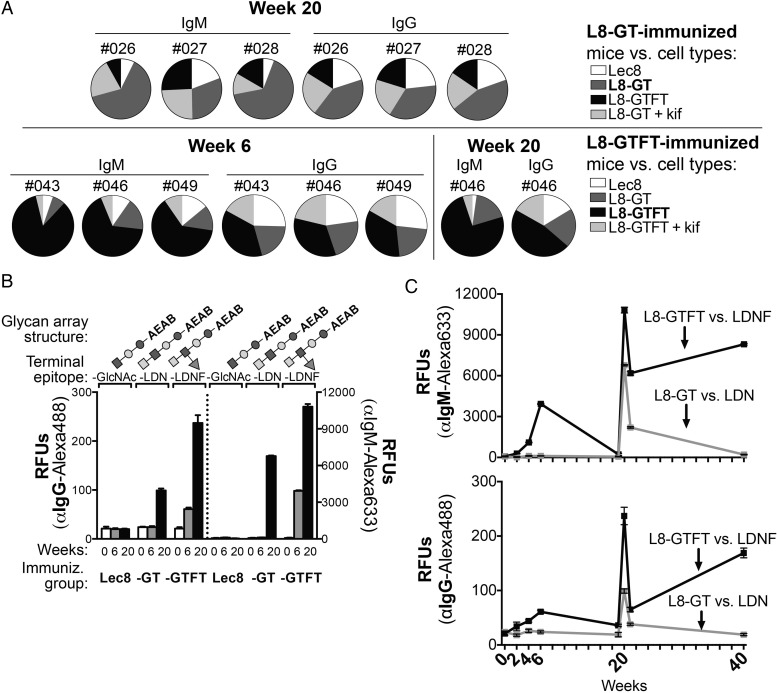
L8-GTFT cells induce long-lasting IgM and IgG antibodies specific for LDNF glycan. (A) Sera from individual L8-GT- (top) and L8-GTFT-immunized (bottom) mice was run on flow cytometry against heterologous cell types (Lec8, white; L8-GT, dark gray; L8-GTFT, black; L8-GT or L8-GTFT treated with kifunensine, light gray) to assess specificity of the response. Individual mouse numbers, isotype and week of the serum sample are indicated above each pie chart, in which the relative binding to each cell type (each slice) is represented as a portion of the sum of geoMFIs of binding for all the cell types (whole pie). Note that naïve serum was also run on each cell type as a negative control, with similar binding to all cell types. (B) The pooled antisera from weeks 0 (white bars), 6 (gray bars) and 20 (black bars) was run on glycan microarrays to assess glycan-specific binding of serum IgG (left y-axis) an IgM (right y-axis). Glycan array structures derived from LNnT, terminating in GlcNAc (glycan ID 13) or with a single unit of LDN (ID 14) or LDNF (ID 16) were printed at 100uM and are shown above each group of bars. Glycan IDs and monosaccharide symbols correspond to Figure 5A, which depicts the entire glycan array with controls—only three selected structures are shown in this figure. Binding is representative of two experiments. (C) Pooled sera from L8-GT (gray) and L8-GTFT-immunized (black) mice at all time points and binding to LDN and LDNF is shown, representative of two experiments. The mean RFUs ± SD are plotted for binding to six replicate spots of each glycan. Kif, kifunensine; RFUs, relative fluorescence units; -GlcNAc; agalacto-Lacto-N-neotetraose (LNnT); -LDN, LacdiNAc made by adding GalNAc to agalacto-LNnT; -LDNF, fucosylated LacdiNAc made by adding fucose to -LDN.