Fig. 7.
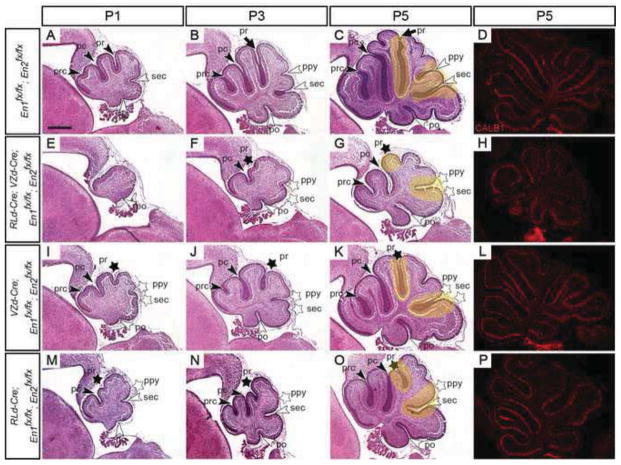
Analysis of a postnatal developmental series of VZ- and RL-derived En1/2 conditional mutants uncovers cell type specific roles in promoting or inhibiting formation of particular fissures. H&E stained sagittal sections of P1 (A, E, I & M), P3 (B, F, J & N) and P5 (C, G, K & O) En1/2 conditional mutant with the indicated genotypes. In VZ- and RL-derived (E–G), or only VZ-derived (I–K) En1/2 conditional mutants formation of the primary and secondary fissures is preferentially disrupted. Conditional inactivation of En1/2 in RL-derived cells (M–O) preferentially disrupts the primary and prepyramidal fissures. Yellow highlighted areas denote regions with defects in mutants compared to same region in the control. Immunostaining for CALB at P5 (D, H, L & P) shows a Purkinje cell monolayer in control and En1/2 conditional mutants. pc, preculminate; po, posterolateral; prc, precentral; ppy, prepyramidal; pr, primary; sec, secondary; black arrowheads, vermal anterior fissures; white arrowheads, vermal posterior fissures. Stars denote fissures with developmental defects. Scale bar: 400μm.