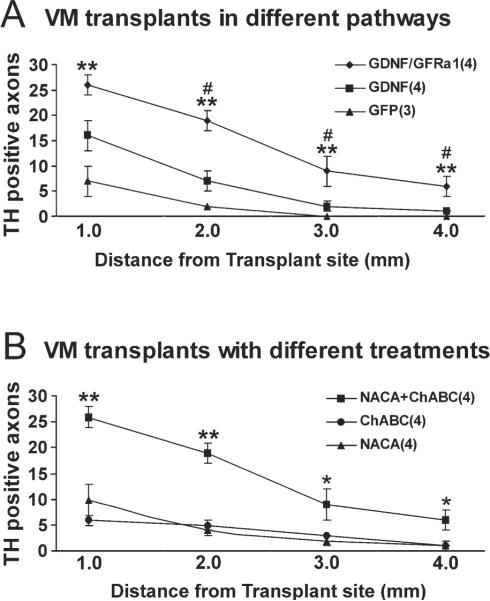
Fig. 5.
A: More axons grew along pathways of GDNF/GFRα1 than GDNF or GFP. With ChABC and NACA treatment, the GDNF/GFRα1 pathway supported the growth of more axons from the transplant along the pathway, across the midline, and toward the contralateral side. Significantly higher numbers of TH+ axons were found in the GDNF/GFRα1 treatment group at almost all pathway points compared with GDNF and GFP pathways, with GDNF at 1.0 mm from the transplantation site being the only nonsignificant point P = 0.065. There was also no significant difference between GDNF and GFP pathways at any points (P > 0.05). # P < 0.05 for GDNF/GFRα1 vs. GDNF; ★ P < 0.01 for GDNF/GFRα1 vs. GFP. B: Combination of GDNF/GFRα1, ChABC, and NACA is required to promote robust growth. Along the GDNF/GFRα1 pathway, a single treatment with ChABC or NACA did not support robust TH+ axons outgrowth along the pathway. However, combining ChABC with NACA significantly increased the number of TH+ axons at all points on both transplantation side and contralateral side. All error bars are standard error of the mean. ★P < 0.01, ★★P < 0.01 for GDNF/GFRα1 vs. ChABC or NACA.